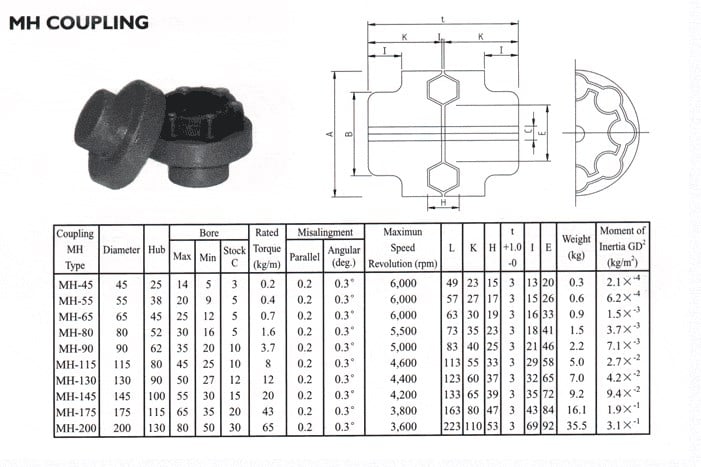
Product Description
Flexible flex Fluid Chain Jaw flange Gear Rigid Spacer PIN HRC MH NM universal Fenaflex Oldham spline clamp tyre grid hydraulic servo motor shaft Coupling
Product Description
The function of Shaft coupling:
1. Shafts for connecting separately manufactured units such as motors and generators.
2. If any axis is misaligned.
3. Provides mechanical flexibility.
4. Absorb the transmission of impact load.
5. Prevent overload
We can provide the following couplings.
| Rigid coupling | Flange coupling | Oldham coupling |
| Sleeve or muff coupling | Gear coupling | Bellow coupling |
| Split muff coupling | Flexible coupling | Fluid coupling |
| Clamp or split-muff or compression coupling | Universal coupling | Variable speed coupling |
| Bushed pin-type coupling | Diaphragm coupling | Constant speed coupling |
Company Profile
We are an industrial company specializing in the production of couplings. It has 3 branches: steel casting, forging, and heat treatment. Main products: cross shaft universal coupling, drum gear coupling, non-metallic elastic element coupling, rigid coupling, etc.
The company mainly produces the industry standard JB3241-91 swap JB5513-91 swc. JB3242-93 swz series universal coupling with spider type. It can also design and produce various non-standard universal couplings, other couplings, and mechanical products for users according to special requirements. Currently, the products are mainly sold to major steel companies at home and abroad, the metallurgical steel rolling industry, and leading engine manufacturers, with an annual production capacity of more than 7000 sets.
The company’s quality policy is “quality for survival, variety for development.” In August 2000, the national quality system certification authority audited that its quality assurance system met the requirements of GB/T19002-1994 IDT ISO9002:1994 and obtained the quality system certification certificate with the registration number 0900B5711. It is the first enterprise in the coupling production industry in HangZhou City that passed the ISO9002 quality and constitution certification.
The company pursues the business purpose of “reliable quality, the supremacy of reputation, commitment to business and customer satisfaction” and welcomes customers at home and abroad to choose our products.
At the same time, the company has established long-term cooperative relations with many enterprises and warmly welcomes friends from all walks of life to visit, investigate and negotiate business!
How to use the coupling safely
The coupling is an intermediate connecting part of each motion mechanism, which directly impacts the regular operation of each motion mechanism. Therefore, attention must be paid to:
1. The coupling is not allowed to have more than the specified axis deflection and radial displacement so as not to affect its transmission performance.
2. The bolts of the LINS coupling shall not be loose or damaged.
3. Gear coupling and cross slide coupling shall be lubricated regularly, and lubricating grease shall be added every 2-3 months to avoid severe wear of gear teeth and serious consequences.
4. The tooth width contact length of gear coupling shall not be less than 70%; Its axial displacement shall not be more significant than 5mm
5. The coupling is not allowed to have cracks. If there are cracks, it needs to be replaced (they can be knocked with a small hammer and judged according to the sound).
6. The keys of LINS coupling shall be closely matched and shall not be loosened.
7. The tooth thickness of the gear coupling is worn. When the lifting mechanism exceeds 15% of the original tooth thickness, the operating mechanism exceeds 25%, and the broken tooth is also scrapped.
8. If the elastic ring of the pin coupling and the sealing ring of the gear coupling is damaged or aged, they should be replaced in time.
Certifications
Packaging & Shipping
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Nonstandard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 19-32 |
| Torque: | <10N.M |
| Bore Diameter: | 19mm |
| Speed: | 8000r/M |
| Structure: | Rigid |
| Samples: |
US$ 999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
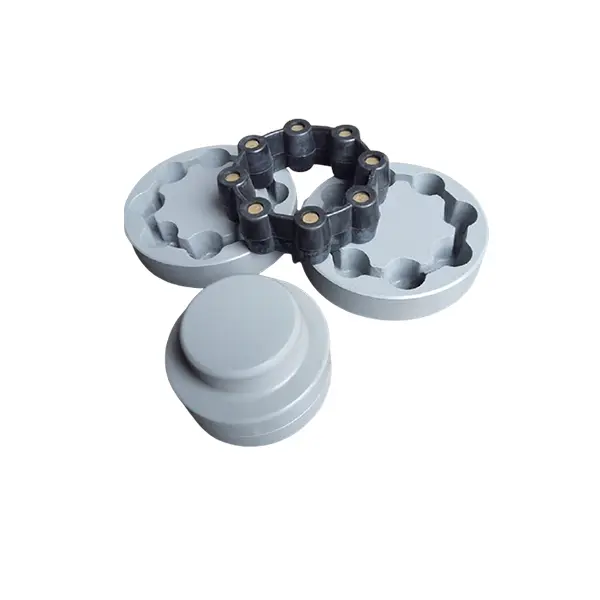

Can flexible couplings accommodate high torque and high-speed applications?
Yes, flexible couplings can accommodate both high torque and high-speed applications, but the suitability depends on the specific design and material of the flexible coupling. Different types of flexible couplings have varying torque and speed capacities, and it’s crucial to select the right type of coupling based on the application requirements.
High Torque Applications:
Some flexible couplings, such as gear couplings and disc couplings, are designed to handle high torque levels. Gear couplings consist of toothed hubs that mesh with each other, providing a robust and efficient torque transmission. They are commonly used in heavy-duty industrial applications, such as steel mills, mining equipment, and power generation plants, where high torque loads are prevalent.
Disc couplings are also suitable for high torque applications. They use a series of flexible metal discs that can handle significant torque while compensating for misalignment. Disc couplings are often used in high-speed machinery and critical applications where precise torque transmission is essential.
High-Speed Applications:
Flexible couplings can also be used in high-speed applications. For instance, certain disc couplings, elastomeric couplings, and grid couplings are capable of handling high rotational speeds. These couplings have low inertia, which means they can respond quickly to changes in speed and provide efficient power transmission at high RPMs.
Elastomeric couplings, such as jaw couplings and tire couplings, are commonly used in various industrial applications, including pumps, compressors, and fans, where both torque and speed requirements are high. They offer good flexibility and damping properties, making them suitable for applications with high-speed variations and vibrations.
Considerations:
When selecting a flexible coupling for high torque and high-speed applications, several factors should be considered:
- The torque and speed ratings provided by the coupling manufacturer should be checked to ensure they meet or exceed the application’s requirements.
- The design and materials of the coupling should be suitable for the specific operating conditions, including temperature, environment, and potential exposure to corrosive substances.
- Proper alignment and installation of the coupling are critical to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature wear.
- In some cases, it may be necessary to use additional components, such as torque limiters or speed reducers, to protect the coupling and the connected equipment from excessive loads or speed fluctuations.
In conclusion, flexible couplings can indeed accommodate high torque and high-speed applications, but the appropriate coupling type and proper selection are essential to ensure reliable and efficient performance in these demanding conditions.
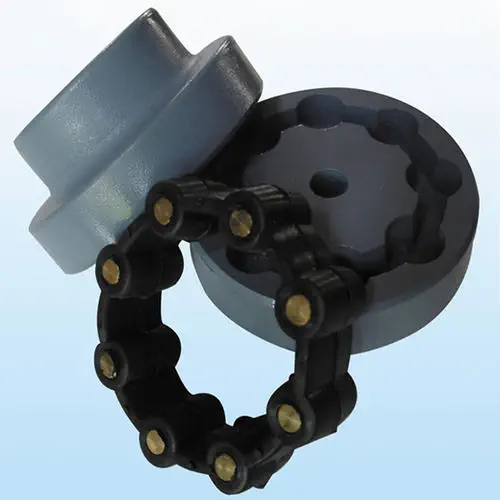

Can flexible couplings be used in corrosive or harsh environments?
Yes, flexible couplings can be designed and selected to be used in corrosive or harsh environments. The choice of materials and coatings plays a crucial role in ensuring the coupling’s durability and performance under challenging conditions.
Corrosion-Resistant Materials:
In corrosive environments, it is essential to use materials that can withstand chemical attacks and oxidation. Stainless steel, specifically grades like 316 or 17-4 PH, is commonly chosen for flexible couplings in such situations. Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications where the coupling may come into contact with corrosive substances or moisture.
Special Coatings:
For certain harsh environments, coupling manufacturers may apply special coatings to enhance the coupling’s corrosion resistance. Examples of coatings include zinc plating, nickel plating, or epoxy coatings. These coatings provide an additional layer of protection against corrosive agents and help extend the coupling’s lifespan.
Sealed Designs:
In environments where the coupling is exposed to contaminants like dust, dirt, or moisture, sealed designs are preferred. Sealed flexible couplings prevent these substances from entering the coupling’s internal components, thus reducing the risk of corrosion and wear. The sealed design also helps to maintain the coupling’s performance over time in challenging conditions.
High-Temperature Applications:
For harsh environments with high temperatures, flexible couplings made from high-temperature resistant materials, such as certain heat-resistant stainless steels or superalloys, can be used. These materials retain their mechanical properties and corrosion resistance even at elevated temperatures.
Chemical Resistance:
For applications where the coupling might encounter chemicals or solvents, it is essential to select a coupling material that is chemically resistant. This prevents degradation and ensures the coupling’s integrity in such environments.
Specialized Designs:
In some cases, where the environment is exceptionally harsh or unique, custom-designed flexible couplings may be necessary. Engineering a coupling to meet the specific demands of the environment ensures optimal performance and reliability.
Consultation with Manufacturers:
When considering flexible couplings for corrosive or harsh environments, it is advisable to consult with coupling manufacturers or engineering experts. They can provide valuable insights and recommend suitable materials, coatings, and designs based on the specific operating conditions.
Summary:
Flexible couplings can indeed be used in corrosive or harsh environments, provided the appropriate materials, coatings, and designs are chosen. Stainless steel, sealed designs, and special coatings are some of the solutions that enhance the coupling’s corrosion resistance and performance. It is essential to consider the specific environment and application requirements when selecting a flexible coupling to ensure optimal functionality and durability in challenging conditions.

What is a flexible coupling and how does it work?
A flexible coupling is a mechanical device used to connect two shafts while allowing for relative movement between them. It is designed to transmit torque from one shaft to another while compensating for misalignment, vibration, and shock. Flexible couplings are essential components in various rotating machinery and systems, as they help protect the connected equipment and enhance overall performance.
Types of Flexible Couplings:
There are several types of flexible couplings, each with its unique design and characteristics. Some common types include:
- Jaw Couplings: Jaw couplings feature elastomer spiders that fit between two hubs. They can accommodate angular and parallel misalignment while dampening vibrations.
- Disc Couplings: Disc couplings use thin metallic discs to connect the shafts. They are highly flexible and provide excellent misalignment compensation.
- Gear Couplings: Gear couplings use gear teeth to transmit torque. They offer high torque capacity and can handle moderate misalignment.
- Beam Couplings: Beam couplings use a single piece of flexible material, such as a metal beam, to transmit torque while compensating for misalignment.
- Bellows Couplings: Bellows couplings use a bellows-like structure to allow for axial, angular, and parallel misalignment compensation.
- Oldham Couplings: Oldham couplings use three discs, with the middle one having a perpendicular slot to allow for misalignment compensation.
How a Flexible Coupling Works:
The operation of a flexible coupling depends on its specific design, but the general principles are similar. Let’s take the example of a jaw coupling to explain how a flexible coupling works:
- Two shafts are connected to the coupling hubs on either side, with an elastomer spider placed between them.
- When torque is applied to one shaft, it causes the spider to compress and deform slightly, transmitting the torque to the other shaft.
- In case of misalignment between the shafts, the elastomer spider flexes and compensates for the misalignment, ensuring smooth torque transmission without imposing excessive loads on the shafts or connected equipment.
- The elastomer spider also acts as a damping element, absorbing vibrations and shocks during operation, which reduces wear on the equipment and enhances system stability.
Overall, the flexibility and ability to compensate for misalignment are the key features that allow a flexible coupling to function effectively. The choice of a specific flexible coupling type depends on the application’s requirements, such as torque capacity, misalignment compensation, and environmental conditions.


editor by CX 2024-04-10
China OEM Flexible Gear Coupling Fluid Flange HRC Spacer Pin Mh Rigid Nm Jaw Steel Chain Brake Standard Drum Wheel Rolling Shaft Steel Transmission Parts
Product Description
Gear coupling flexible Fluid Flange HRC Spacer PIN MH Rigid NM Jaw Steel chain brake standard drum wheel rolling shaft steel transmission parts
Ever-Power industry is 1 of the biggest couplings manufacturer in China, have already exported lots of gear couplings, Jaw couplings, chain couplings etc.. to Japan, Korea, Italy , USA …..
Application of Gear coupling
Gear couplings are used to connect 2 shafts that are not perfectly aligned. They do this by using gears to transmit torque between the shafts. Gear couplings are available in a variety of sizes and types, and they are used in a wide range of applications.
Some of the most common applications for gear couplings include:
- Pumps: Gear couplings are used to connect the motor to the pump in a variety of pumps, including centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps, and gear pumps.
- Fans: Gear couplings are used to connect the motor to the fan in a variety of fans, including centrifugal fans, axial fans, and propeller fans.
- Compressors: Gear couplings are used to connect the motor to the compressor in a variety of compressors, including reciprocating compressors, rotary screw compressors, and centrifugal compressors.
- Machine tools: Gear couplings are used to connect the motor to the machine tool in a variety of machine tools, including lathes, mills, and drills.
- Conveyors: Gear couplings are used to connect the motor to the conveyor in a variety of conveyors, including belt conveyors, bucket conveyors, and screw conveyors.
Gear couplings offer a number of advantages over other types of couplings, including:
- High torque capacity: Gear couplings can transmit high torque, which is necessary for applications where a lot of force needs to be applied.
- Good alignment tolerance: Gear couplings can tolerate misalignment, which is necessary for applications where the shafts may not be perfectly aligned.
- Long life: Gear couplings have a long life, which is necessary for applications where the coupling needs to operate for a long time.
- Low noise: Gear couplings operate quietly, which is important for applications where noise is a concern.
- Versatility: Gear couplings can be used in a variety of applications.
If you need a coupling that can transmit high torque, tolerate misalignment, and have a long life, then a gear coupling may be the right solution for you.
thumb_upthumb_down
uploa
Main range of Couplings
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | – |
| Torque: | – |
| Bore Diameter: | – |
| Speed: | – |
| Structure: | – |
| Samples: |
US$ 999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
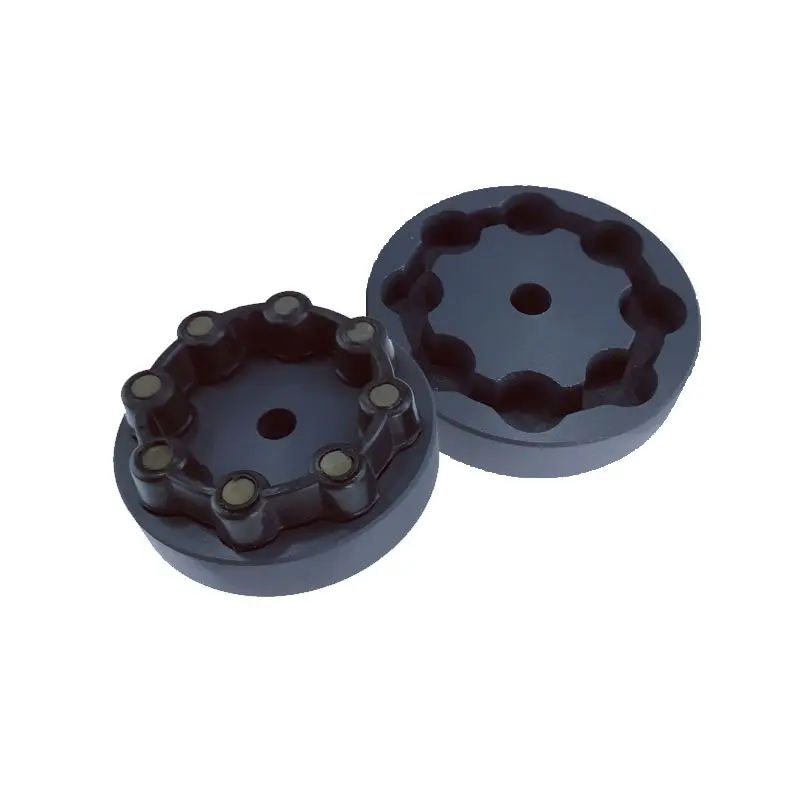


What are the maintenance requirements for flexible couplings?
Maintenance of flexible couplings is essential to ensure their reliable and efficient performance over their service life. Proper maintenance helps prevent premature wear, reduces the risk of unexpected failures, and extends the lifespan of the couplings. Here are some key maintenance requirements for flexible couplings:
- Regular Inspection: Perform regular visual inspections of the flexible couplings to check for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Look for cracks, tears, or any other visible issues in the coupling components.
- Lubrication: Some flexible couplings, especially those with moving parts or sliding surfaces, may require periodic lubrication. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding the type and frequency of lubrication to ensure smooth operation.
- Alignment Checks: Misalignment is a common cause of coupling failure. Regularly check the alignment of the connected shafts and adjust as necessary. Proper alignment reduces stress on the coupling and improves power transmission efficiency.
- Torque Monitoring: Monitoring the torque transmitted through the coupling can help detect any abnormal or excessive loads. If the coupling is subjected to loads beyond its rated capacity, it may lead to premature failure.
- Environmental Protection: If the couplings are exposed to harsh environmental conditions, take measures to protect them from dust, dirt, moisture, and corrosive substances. Consider using protective covers or seals to shield the couplings from potential contaminants.
- Temperature Considerations: Ensure that the operating temperature of the flexible coupling is within its designed range. Excessive heat can accelerate wear, while extremely low temperatures may affect the flexibility of certain coupling materials.
- Replace Worn or Damaged Parts: If any components of the flexible coupling show signs of wear or damage, replace them promptly with genuine replacement parts from the manufacturer.
- Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Follow the maintenance guidelines provided by the coupling manufacturer. They often include specific maintenance intervals and procedures tailored to the coupling’s design and materials.
- Training and Expertise: Ensure that maintenance personnel have the necessary training and expertise to inspect and maintain the flexible couplings properly. Improper maintenance practices can lead to further issues and compromise the coupling’s performance.
By adhering to these maintenance requirements, you can maximize the service life of the flexible couplings and minimize the risk of unexpected downtime or costly repairs. Regular maintenance helps maintain the efficiency and reliability of the coupling in various industrial, automotive, and machinery applications.

How does a flexible coupling handle angular, parallel, and axial misalignment?
A flexible coupling is designed to accommodate various types of misalignment between two rotating shafts: angular misalignment, parallel misalignment, and axial misalignment. The flexibility of the coupling allows it to maintain a connection between the shafts while compensating for these misalignment types. Here’s how a flexible coupling handles each type of misalignment:
- Angular Misalignment: Angular misalignment occurs when the axes of the two shafts are not collinear and form an angle with each other. Flexible couplings can handle angular misalignment by incorporating an element that can flex and bend. One common design is the “spider” or “jaw” element, which consists of elastomeric materials. As the shafts are misaligned, the elastomeric element can deform slightly, allowing the coupling to accommodate the angular offset between the shafts while still transmitting torque.
- Parallel Misalignment: Parallel misalignment, also known as offset misalignment, occurs when the axes of the two shafts are parallel but not perfectly aligned with each other. Flexible couplings can handle parallel misalignment through the same elastomeric element. The flexible nature of the element enables it to shift and adjust to the offset between the shafts, ensuring continuous power transmission while minimizing additional stresses on the machinery.
- Axial Misalignment: Axial misalignment, also called end-play misalignment, occurs when the two shafts move closer together or farther apart along their common axis. Flexible couplings can handle axial misalignment through specific designs that allow limited axial movement. For instance, some couplings use slotted holes or a floating member that permits axial displacement while maintaining the connection between the shafts.
By providing the capability to handle angular, parallel, and axial misalignment, flexible couplings offer several advantages for power transmission systems:
- They help to prevent premature wear and damage to the connected equipment, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
- They minimize vibration and shock loads, enhancing the overall smoothness and reliability of the machinery.
- They reduce the risk of equipment failure due to misalignment-induced stresses, improving the system’s operational life.
- They allow for easier installation and alignment adjustments, saving time and effort during setup and maintenance.
Overall, flexible couplings play a crucial role in handling misalignment and ensuring efficient power transmission in various industrial applications.

What are the advantages of using flexible couplings in mechanical systems?
Flexible couplings offer several advantages in mechanical systems, making them essential components in various applications. Here are the key advantages of using flexible couplings:
- Misalignment Compensation: One of the primary advantages of flexible couplings is their ability to compensate for shaft misalignment. In mechanical systems, misalignment can occur due to various factors such as installation errors, thermal expansion, or shaft deflection. Flexible couplings can accommodate angular, parallel, and axial misalignment, ensuring smooth power transmission and reducing stress on the connected equipment and shafts.
- Vibration Damping: Flexible couplings act as damping elements, absorbing and dissipating vibrations and shocks generated during operation. This feature helps to reduce noise, protect the equipment from excessive wear, and enhance overall system reliability and performance.
- Torsional Flexibility: Flexible couplings provide torsional flexibility, allowing them to handle slight angular and axial deflections. This capability protects the equipment from sudden torque fluctuations, shock loads, and torque spikes, ensuring smoother operation and preventing damage to the machinery.
- Overload Protection: In case of sudden overloads or torque spikes, flexible couplings can absorb and distribute the excess torque, protecting the connected equipment and drivetrain from damage. This overload protection feature prevents unexpected failures and reduces downtime in critical applications.
- Reduce Wear and Maintenance: By compensating for misalignment and damping vibrations, flexible couplings help reduce wear on the connected equipment, bearings, and seals. This results in extended component life and reduced maintenance requirements, leading to cost savings and improved system reliability.
- Compensation for Thermal Expansion: In systems exposed to temperature variations, flexible couplings can compensate for thermal expansion and contraction, maintaining proper alignment and preventing binding or excessive stress on the equipment during temperature changes.
- Electric Isolation: Some types of flexible couplings, such as disc couplings, offer electrical isolation between shafts. This feature is beneficial in applications where galvanic corrosion or electrical interference between connected components needs to be minimized.
- Space and Weight Savings: Flexible couplings often have compact designs and low inertia, which is advantageous in applications with space constraints and where minimizing weight is crucial for performance and efficiency.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Flexible couplings are generally cost-effective solutions for power transmission and motion control, especially when compared to more complex and expensive coupling types. Their relatively simple design and ease of installation contribute to cost savings.
In summary, flexible couplings play a vital role in mechanical systems by providing misalignment compensation, vibration damping, overload protection, and torsional flexibility. These advantages lead to improved system performance, reduced wear and maintenance, and enhanced equipment reliability, making flexible couplings a preferred choice in various industrial, automotive, marine, and aerospace applications.


editor by CX 2023-09-07
China supplier Gear Coupling Flexible Fluid Flange HRC Spacer Pin Mh Rigid Nm Jaw Steel Chain Brake Standard Drum Wheel Rolling Shaft Steel Transmission Parts
Product Description
Gear coupling flexible Fluid Flange HRC Spacer PIN MH Rigid NM Jaw Steel chain brake standard drum wheel rolling shaft steel transmission parts
Ever-Power industry is 1 of the biggest couplings manufacturer in China, have already exported lots of gear couplings, Jaw couplings, chain couplings etc.. to Japan, Korea, Italy , USA …..
Application of Gear coupling
Gear couplings are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Pumps
- Compressors
- Fans
- Generators
- Wind turbines
- Conveyors
- Mixers
- Mills
- Machine tools
- Vehicles
Gear couplings are used to transmit power between 2 shafts that are not perfectly aligned. They can also be used to absorb shock and vibration, and to protect the equipment from damage.
There are many different types of gear couplings available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The type of coupling that is best for a particular application will depend on the size and type of equipment, the amount of power that needs to be transmitted, and the environment in which the equipment will be used.
Here are some of the benefits of using gear couplings:
- High efficiency: Gear couplings are very efficient at transmitting power. This is due to the fact that the gears in the coupling help to reduce friction.
- Long life: Gear couplings are very durable and can last for many years with proper maintenance.
- Low maintenance: Gear couplings require very little maintenance. This is because they are self-lubricating and do not need to be greased or oiled.
- Wide range of applications: Gear couplings can be used in a wide variety of applications. This makes them a versatile and cost-effective option for many businesses.
If you are looking for a reliable and efficient means of power transmission, gear couplings are a great option. They are available in a wide range of sizes and styles to meet the needs of different applications. Gear couplings are also relatively inexpensive, making them a cost-effective choice.
Main range of Couplings
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | – |
| Torque: | – |
| Bore Diameter: | – |
| Speed: | – |
| Structure: | – |
| Samples: |
US$ 999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|


Can flexible couplings be used in both horizontal and vertical shaft arrangements?
Yes, flexible couplings can be used in both horizontal and vertical shaft arrangements. The design of flexible couplings allows them to accommodate misalignment and compensate for angular, parallel, and axial displacements between the shafts, making them suitable for various shaft orientations.
Horizontal Shaft Arrangements:
In horizontal shaft arrangements, where the shafts are parallel to the ground or horizontal plane, flexible couplings are commonly used to connect two rotating shafts. These couplings help transmit torque from one shaft to another while accommodating any misalignment that may occur during operation. Horizontal shaft arrangements are common in applications such as pumps, compressors, conveyors, and industrial machinery.
Vertical Shaft Arrangements:
In vertical shaft arrangements, where the shafts are perpendicular to the ground or vertical plane, flexible couplings are also applicable. Vertical shafts often require couplings that can handle the additional weight and forces resulting from gravity. Flexible couplings designed for vertical applications can support the weight of the rotating equipment while allowing for some axial movement to accommodate thermal expansion or other displacements. Vertical shaft arrangements are commonly found in applications such as pumps, gearboxes, turbines, and some marine propulsion systems.
Considerations for Vertical Shaft Arrangements:
When using flexible couplings in vertical shaft arrangements, there are a few additional considerations to keep in mind:
- Thrust Load: Vertical shafts can generate thrust loads, especially in upward or downward direction. The flexible coupling should be selected based on its capacity to handle both radial and axial loads to accommodate these forces.
- Lubrication: Some vertical couplings may require additional lubrication to ensure smooth operation and reduce wear, particularly if they are exposed to high axial loads or extended vertical shafts.
- Support and Bearing: Proper support and bearing arrangements for the vertical shaft are essential to prevent excessive shaft deflection and ensure the flexible coupling functions correctly.
Overall, flexible couplings are versatile and adaptable to various shaft orientations, providing efficient power transmission and misalignment compensation. Whether in horizontal or vertical arrangements, using the appropriate flexible coupling design and considering the specific application requirements will help ensure reliable and efficient operation.

What are the differences between elastomeric and metallic flexible coupling designs?
Elastomeric and metallic flexible couplings are two distinct designs used to transmit torque and accommodate misalignment in mechanical systems. Each type offers unique characteristics and advantages, making them suitable for different applications.
Elastomeric Flexible Couplings:
Elastomeric flexible couplings, also known as flexible or jaw couplings, employ an elastomeric material (rubber or similar) as the flexible element. The elastomer is typically molded between two hubs, and it acts as the connector between the driving and driven shafts. The key differences and characteristics of elastomeric couplings include:
- Misalignment Compensation: Elastomeric couplings are designed to handle moderate levels of angular, parallel, and axial misalignment. The elastomeric material flexes to accommodate the misalignment while transmitting torque between the shafts.
- Vibration Damping: The elastomeric material in these couplings offers excellent vibration dampening properties, reducing the transmission of vibrations from one shaft to another. This feature helps protect connected equipment from excessive vibrations and enhances system reliability.
- Shock Load Absorption: Elastomeric couplings can absorb and dampen shock loads, protecting the system from sudden impacts or overloads.
- Cost-Effective: Elastomeric couplings are generally more cost-effective compared to metallic couplings, making them a popular choice for various industrial applications.
- Simple Design and Installation: Elastomeric couplings often have a straightforward design, allowing for easy installation and maintenance.
- Lower Torque Capacity: These couplings have a lower torque capacity compared to metallic couplings, making them suitable for applications with moderate torque requirements.
- Common Applications: Elastomeric couplings are commonly used in pumps, compressors, fans, conveyors, and other applications that require moderate torque transmission and misalignment compensation.
Metallic Flexible Couplings:
Metallic flexible couplings use metal components (such as steel, stainless steel, or aluminum) to connect the driving and driven shafts. The metallic designs can vary significantly depending on the type of metallic coupling, but some general characteristics include:
- High Torque Capacity: Metallic couplings have higher torque transmission capabilities compared to elastomeric couplings. They are well-suited for applications requiring high torque handling.
- Misalignment Compensation: Depending on the design, some metallic couplings can accommodate minimal misalignment, but they are generally not as flexible as elastomeric couplings in this regard.
- Stiffer Construction: Metallic couplings are generally stiffer than elastomeric couplings, offering less vibration dampening but higher torsional stiffness.
- Compact Design: Metallic couplings can have a more compact design, making them suitable for applications with limited space.
- Higher Precision: Metallic couplings often offer higher precision and concentricity, resulting in better shaft alignment.
- Higher Cost: Metallic couplings are typically more expensive than elastomeric couplings due to their construction and higher torque capacity.
- Common Applications: Metallic couplings are commonly used in high-speed machinery, precision equipment, robotics, and applications with high torque requirements.
Summary:
In summary, the main differences between elastomeric and metallic flexible coupling designs lie in their flexibility, torque capacity, vibration dampening, cost, and applications. Elastomeric couplings are suitable for applications with moderate torque, misalignment compensation, and vibration dampening requirements. On the other hand, metallic couplings are chosen for applications with higher torque and precision requirements, where flexibility and vibration dampening are less critical.

What is a flexible coupling and how does it work?
A flexible coupling is a mechanical device used to connect two shafts while allowing for relative movement between them. It is designed to transmit torque from one shaft to another while compensating for misalignment, vibration, and shock. Flexible couplings are essential components in various rotating machinery and systems, as they help protect the connected equipment and enhance overall performance.
Types of Flexible Couplings:
There are several types of flexible couplings, each with its unique design and characteristics. Some common types include:
- Jaw Couplings: Jaw couplings feature elastomer spiders that fit between two hubs. They can accommodate angular and parallel misalignment while dampening vibrations.
- Disc Couplings: Disc couplings use thin metallic discs to connect the shafts. They are highly flexible and provide excellent misalignment compensation.
- Gear Couplings: Gear couplings use gear teeth to transmit torque. They offer high torque capacity and can handle moderate misalignment.
- Beam Couplings: Beam couplings use a single piece of flexible material, such as a metal beam, to transmit torque while compensating for misalignment.
- Bellows Couplings: Bellows couplings use a bellows-like structure to allow for axial, angular, and parallel misalignment compensation.
- Oldham Couplings: Oldham couplings use three discs, with the middle one having a perpendicular slot to allow for misalignment compensation.
How a Flexible Coupling Works:
The operation of a flexible coupling depends on its specific design, but the general principles are similar. Let’s take the example of a jaw coupling to explain how a flexible coupling works:
- Two shafts are connected to the coupling hubs on either side, with an elastomer spider placed between them.
- When torque is applied to one shaft, it causes the spider to compress and deform slightly, transmitting the torque to the other shaft.
- In case of misalignment between the shafts, the elastomer spider flexes and compensates for the misalignment, ensuring smooth torque transmission without imposing excessive loads on the shafts or connected equipment.
- The elastomer spider also acts as a damping element, absorbing vibrations and shocks during operation, which reduces wear on the equipment and enhances system stability.
Overall, the flexibility and ability to compensate for misalignment are the key features that allow a flexible coupling to function effectively. The choice of a specific flexible coupling type depends on the application’s requirements, such as torque capacity, misalignment compensation, and environmental conditions.


editor by CX 2023-08-04
China Standard Gicl Gear Coupling for Rolling Mill with Best Sales
Solution Description
High quality IS OUR Tradition!!!!!
This shaft coupling is suited for the joint of 2 level coacial traces, and has the transmissive shafting of particular angular displacement. The transmission nominal torque is .8~3200KN·m, and the temperature of functioning problem is -20~+80ºC
Its products apply extensively in transportataion, metallurgy, chemical sector, mine, developing building, hoist and other industries and equipments, and provide for a variety of significant industries yr by 12 months.
| Model | Nominal Torque Tn/N.m |
Speed [n] r/min |
Shaft Hole Dia | Shaft Hole Size |
D | D1 | A | C | C1 | C2 | Rotational InertiaKg |
Grease ml |
Weight Kg |
|
| Y | Z1,J1 | |||||||||||||
| d1,d2,d3 | L | |||||||||||||
| GICL1 | 630 | 7100 | sixteen,18,19 | 42 | – | 125 | 95 | 75 | 20 | – | – | 0.009 | 55 | 5.9 |
| 20,22,24 | fifty two | 38 | – | 24 | ||||||||||
| twenty five,28 | 62 | forty four | 10 | – | 19 | |||||||||
| 30,32,35,38 | eighty two | sixty | 2.5 | 15 | 22 | |||||||||
| GICL2 | 1120 | 6300 | 25,28 | 62 | 44 | 144 | 120 | 88 | 10.5 | – | 29 | 0.02 | 100 | 9.seven |
| thirty,32,35,38 | eighty two | 60 | twelve.5 | thirty | ||||||||||
| 40,forty two,45,forty eight | 112 | 84 | two.5 | thirteen.five | 28 | |||||||||
| GICL3 | 2240 | 5900 | 30,32,35,38 | eighty two | sixty | 174 | 140 | 106 | 3 | 24.5 | 25 | 0.047 | 140 | 17.two |
| forty,42,forty five,forty eight,50,55,56 | 112 | eighty four | 17 | 28 | ||||||||||
| sixty | 142 | 107 | 35 | |||||||||||
| GICL4 | 3600 | 5400 | 32,35,38 | 82 | sixty | 196 | 165 | 125.five | 14 | 37 | 32 | 0.091 | 170 | 24.9 |
| 40,42,forty five,forty eight,fifty,fifty five,fifty six | 112 | 84 | 28 | |||||||||||
| sixty,sixty three,65,70 | 142 | 107 | 3 | 17 | 35 | |||||||||
| GICL5 | 5000 | 5000 | forty,forty two,forty five,48,fifty,55,fifty six | 112 | eighty four | 224 | 183 | 142 | 3 | twenty five | 28 | 0.167 | 270 | 38 |
| 60 63 65 70 71 75 | 142 | 107 | 20 | 35 | ||||||||||
| 80 | 172 | 132 | 22 | 43 | ||||||||||
| GICL6 | 7100 | 4800 | 48 50 55 56 | 112 | eighty four | 241 | 200 | 160 | 6 | 35 | 35 | 0.267 | 380 | 48.two |
| 60 63 65 70 71 75 | 142 | 107 | 20 | 35 | ||||||||||
| 80 85 90 | 172 | 132 | 4 | 22 | 43 | |||||||||
| GICL7 | 10000 | 4500 | 60 63 65 70 71 75 | 142 | 107 | 260 | 230 | 180 | 4 | 35 | 35 | 0.453 | 570 | 68.9 |
| 80 85 90 95 | 172 | 132 | 22 | 43 | ||||||||||
| 100 | 212 | 167 | forty eight | |||||||||||
| GICL8 | 14000 | 4000 | 65 70 71 75 | 142 | 107 | 282 | 245 | 193 | 5 | 35 | 35 | 0.646 | 660 | 83.three |
| 80 85 90 95 | 172 | 132 | 22 | forty three | ||||||||||
| 100 110 | 212 | 167 | 48 | |||||||||||
| GICL9 | 18000 | 3500 | 70 71 75 | 142 | 107 | 314 | 270 | 208 | 10 | 45 | 45 | 1.036 | 700 | 110 |
| 80 85 90 95 | 172 | 132 | ||||||||||||
| 100 110 120 125 | 212 | 167 | 5 | 22 | 43 | |||||||||
| 49 | ||||||||||||||
| GICL10 | 31500 | 3200 | 80 85 90 95 | 172 | 132 | 346 | 300 | 249 | 5 | forty three | 43 | 1.88 | 900 | 157 |
| 100 110 120 125 | 212 | 167 | 22 | 49 | ||||||||||
| 130 140 | 252 | 202 | 29 | fifty four | ||||||||||
| GICL11 | 40000 | 3000 | 100 110 120 125 | 212 | 167 | 380 | 330 | 267 | 6 | 29 | 49 | 3.28 | 1200 | 217 |
| 130 140 150 | 252 | 202 | 54 | |||||||||||
| 160 | 302 | 242 | 64 | |||||||||||
| GICL12 | 56000 | 2600 | 120 125 | 212 | 167 | 442 | 380 | 313 | 6 | fifty seven | fifty seven | 5.08 | 2000 | 305 |
| 130 140 150 | 252 | 202 | 29 | 55 | ||||||||||
| 160 170 180 | 302 | 242 | sixty eight | |||||||||||
| GICL13 | 80000 | 2300 | 140 150 | 252 | 202 | 482 | 420 | 364 | 7 | fifty four | fifty seven | 10.06 | 3000 | 419 |
| 160 170 180 | 302 | 242 | 32 | 70 | ||||||||||
| 190 200 | 352 | 282 | eighty | |||||||||||
| GICL14 | 112000 | 2100 | 160 170 180 | 302 | 242 | 520 | 465 | 415 | 8 | forty two | 70 | 16.774 | 4500 | 594 |
| 190 200 220 | 352 | 282 | 32 | eighty | ||||||||||
| GICL15 | 160000 | 1900 | 190 200 220 | 352 | 282 | 580 | 510 | 429 | 10 | 34 | 80 | 26.fifty five | 5000 | 783 |
| 140 150 | 410 | 330 | 38 | – | ||||||||||
| GICL16 | 250000 | 1600 | 200 220 | 352 | 282 | 680 | 595 | 501 | 10 | fifty eight | eighty | 52.22 | 8000 | 1134 |
| 240 250 260 | 410 | 330 | 38 | – | ||||||||||
| 280 | 470 | 380 | 38 | |||||||||||
| GICL17 | 280000 | 1500 | 220 | 352 | 282 | 720 | 645 | 512 | 10 | 74 | 80 | 69 | 10000 | 1305 |
| 240 250 260 | 410 | 330 | ||||||||||||
| 280 300 | 470 | 380 | 39 | – | ||||||||||
| GICL18 | 355000 | 1400 | 240 250 260 | 410 | 330 | 775 | 675 | 524 | 10 | 46 | – | 96.16 | 11000 | 1626 |
| 280 300 320 | 470 | 380 | 41 | – | ||||||||||
| GICL19 | 450000 | 1300 | 260 | 410 | 330 | 815 | 715 | 560 | 10 | 67 | – | 115.6 | 13000 | 1773 |
| 280 300 320 | 470 | 380 | 41 | |||||||||||
| 340 | 550 | 450 | ||||||||||||
| GICL20 | 500000 | 1200 | 280 300 320 | 470 | 380 | 855 | 755 | 595 | 13 | 44 | – | 167.41 | 16000 | 2263 |
| 340 360 | 550 | 450 | ||||||||||||
| GICL21 | 630000 | 1100 | 300 320 | 470 | 380 | 915 | 795 | 611 | 13 | 59 | – | 215.7 | 20000 | 2593 |
| 340 360 380 | 550 | 450 | 44 | |||||||||||
| GICL22 | 710000 | 950 | 340,360,380 | 550 | 450 | 960 | 840 | 632 | 13 | 44 | – | 278.07 | 26000 | 3036 |
| 400 | 650 | 450 | ||||||||||||
| GICL23 | 800000 | 900 | 360,380 | 550 | 450 | 1571 | 890 | 666 | 13 | 44 | – | 379.four | 29000 | 3668 |
| 400,420 | 650 | 540 | 48 | |||||||||||
| GICL24 | 1000000 | 875 | 380 | 550 | 450 | 1050 | 925 | 685 | 15 | forty six | – | 448.1 | 32000 | 3946 |
| 400,420,450 | 650 | 540 | 50 | |||||||||||
| GICL25 | 1120000 | 850 | 400,420,450,480 | 650 | 540 | 1120 | 970 | 724 | 15 | fifty | – | 564.sixty four | 34000 | 4443 |
| GICL26 | 1250000 | 825 | 420,450,480,500 | 650 | 540 | 1160 | 990 | 733 | 15 | 50 | – | 637.4 | 37000 | 4791 |
| GICL27 | 1400000 | 800 | 450,480,500 | 650 | 540 | 1210 | 1060 | 739 | 15 | 50 | – | 866.26 | 45000 | 5758 |
| 530 | 800 | 680 | ||||||||||||
| GICL28 | 1600000 | 770 | 480,five hundred | 650 | 540 | 1250 | 1080 | 805 | 20 | 55 | – | 1571.76 | 47000 | 6232 |
| 530,560 | 800 | 680 | ||||||||||||
| GICL29 | 2240000 | 725 | five hundred | 650 | 540 | 1340 | 1200 | 798 | 20 | 57 | – | 1450.eighty four | 50000 | 7549 |
| 530,560,600 | 800 | 680 | ||||||||||||
| GICL30 | 2800000 | seven-hundred | 530,560,600,630 | 800 | 680 | 1390 | 1240 | 806 | 20 | fifty five | – | 1974.17 | 59000 | 9514 |
HangZhou CZPT Machinery Co., Ltd is a medium-scale business specialized in the manufacture of shaft coupling and paper-creating equipment with the integration of design, creation and provider.
Orienthold specialized in the creation of a variety of collection couplings, complete have 29 series, much more than 580 types of couplings, this kind of as universal couplings, cardan shafts, equipment couplings, flexible couplings, elastic couplings, plum claw-type couplings, disc couplings, tyre couplings, roller chain couplings and so on. All of our goods are broadly employed in metallurgy, mining, shipbuilding, port, paper producing and large equipment business.
Orienthold offer supporting solutions for many domestic large and center scale Iron and steel businesses, productively concluded more than ten localization assignments of imported coupling generation line.
|
/ Set | |
10 Sets (Min. Order) |
###
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | as Your Requirement |
| Torque: | as Your Requirement |
| Bore Diameter: | as Your Requirement |
| Speed: | 3200~7100 |
| Structure: | Flexible |
###
| Customization: |
|---|
###
| Model | Nominal Torque Tn/N.m |
Speed [n] r/min |
Shaft Hole Dia | Shaft Hole Length |
D | D1 | A | C | C1 | C2 | Rotational InertiaKg |
Grease ml |
Weight Kg |
|
| Y | Z1,J1 | |||||||||||||
| d1,d2,d3 | L | |||||||||||||
| GICL1 | 630 | 7100 | 16,18,19 | 42 | – | 125 | 95 | 75 | 20 | – | – | 0.009 | 55 | 5.9 |
| 20,22,24 | 52 | 38 | – | 24 | ||||||||||
| 25,28 | 62 | 44 | 10 | – | 19 | |||||||||
| 30,32,35,38 | 82 | 60 | 2.5 | 15 | 22 | |||||||||
| GICL2 | 1120 | 6300 | 25,28 | 62 | 44 | 144 | 120 | 88 | 10.5 | – | 29 | 0.02 | 100 | 9.7 |
| 30,32,35,38 | 82 | 60 | 12.5 | 30 | ||||||||||
| 40,42,45,48 | 112 | 84 | 2.5 | 13.5 | 28 | |||||||||
| GICL3 | 2240 | 5900 | 30,32,35,38 | 82 | 60 | 174 | 140 | 106 | 3 | 24.5 | 25 | 0.047 | 140 | 17.2 |
| 40,42,45,48,50,55,56 | 112 | 84 | 17 | 28 | ||||||||||
| 60 | 142 | 107 | 35 | |||||||||||
| GICL4 | 3600 | 5400 | 32,35,38 | 82 | 60 | 196 | 165 | 125.5 | 14 | 37 | 32 | 0.091 | 170 | 24.9 |
| 40,42,45,48,50,55,56 | 112 | 84 | 28 | |||||||||||
| 60,63,65,70 | 142 | 107 | 3 | 17 | 35 | |||||||||
| GICL5 | 5000 | 5000 | 40,42,45,48,50,55,56 | 112 | 84 | 224 | 183 | 142 | 3 | 25 | 28 | 0.167 | 270 | 38 |
| 60 63 65 70 71 75 | 142 | 107 | 20 | 35 | ||||||||||
| 80 | 172 | 132 | 22 | 43 | ||||||||||
| GICL6 | 7100 | 4800 | 48 50 55 56 | 112 | 84 | 241 | 200 | 160 | 6 | 35 | 35 | 0.267 | 380 | 48.2 |
| 60 63 65 70 71 75 | 142 | 107 | 20 | 35 | ||||||||||
| 80 85 90 | 172 | 132 | 4 | 22 | 43 | |||||||||
| GICL7 | 10000 | 4500 | 60 63 65 70 71 75 | 142 | 107 | 260 | 230 | 180 | 4 | 35 | 35 | 0.453 | 570 | 68.9 |
| 80 85 90 95 | 172 | 132 | 22 | 43 | ||||||||||
| 100 | 212 | 167 | 48 | |||||||||||
| GICL8 | 14000 | 4000 | 65 70 71 75 | 142 | 107 | 282 | 245 | 193 | 5 | 35 | 35 | 0.646 | 660 | 83.3 |
| 80 85 90 95 | 172 | 132 | 22 | 43 | ||||||||||
| 100 110 | 212 | 167 | 48 | |||||||||||
| GICL9 | 18000 | 3500 | 70 71 75 | 142 | 107 | 314 | 270 | 208 | 10 | 45 | 45 | 1.036 | 700 | 110 |
| 80 85 90 95 | 172 | 132 | ||||||||||||
| 100 110 120 125 | 212 | 167 | 5 | 22 | 43 | |||||||||
| 49 | ||||||||||||||
| GICL10 | 31500 | 3200 | 80 85 90 95 | 172 | 132 | 346 | 300 | 249 | 5 | 43 | 43 | 1.88 | 900 | 157 |
| 100 110 120 125 | 212 | 167 | 22 | 49 | ||||||||||
| 130 140 | 252 | 202 | 29 | 54 | ||||||||||
| GICL11 | 40000 | 3000 | 100 110 120 125 | 212 | 167 | 380 | 330 | 267 | 6 | 29 | 49 | 3.28 | 1200 | 217 |
| 130 140 150 | 252 | 202 | 54 | |||||||||||
| 160 | 302 | 242 | 64 | |||||||||||
| GICL12 | 56000 | 2600 | 120 125 | 212 | 167 | 442 | 380 | 313 | 6 | 57 | 57 | 5.08 | 2000 | 305 |
| 130 140 150 | 252 | 202 | 29 | 55 | ||||||||||
| 160 170 180 | 302 | 242 | 68 | |||||||||||
| GICL13 | 80000 | 2300 | 140 150 | 252 | 202 | 482 | 420 | 364 | 7 | 54 | 57 | 10.06 | 3000 | 419 |
| 160 170 180 | 302 | 242 | 32 | 70 | ||||||||||
| 190 200 | 352 | 282 | 80 | |||||||||||
| GICL14 | 112000 | 2100 | 160 170 180 | 302 | 242 | 520 | 465 | 415 | 8 | 42 | 70 | 16.774 | 4500 | 594 |
| 190 200 220 | 352 | 282 | 32 | 80 | ||||||||||
| GICL15 | 160000 | 1900 | 190 200 220 | 352 | 282 | 580 | 510 | 429 | 10 | 34 | 80 | 26.55 | 5000 | 783 |
| 140 150 | 410 | 330 | 38 | – | ||||||||||
| GICL16 | 250000 | 1600 | 200 220 | 352 | 282 | 680 | 595 | 501 | 10 | 58 | 80 | 52.22 | 8000 | 1134 |
| 240 250 260 | 410 | 330 | 38 | – | ||||||||||
| 280 | 470 | 380 | 38 | |||||||||||
| GICL17 | 280000 | 1500 | 220 | 352 | 282 | 720 | 645 | 512 | 10 | 74 | 80 | 69 | 10000 | 1305 |
| 240 250 260 | 410 | 330 | ||||||||||||
| 280 300 | 470 | 380 | 39 | – | ||||||||||
| GICL18 | 355000 | 1400 | 240 250 260 | 410 | 330 | 775 | 675 | 524 | 10 | 46 | – | 96.16 | 11000 | 1626 |
| 280 300 320 | 470 | 380 | 41 | – | ||||||||||
| GICL19 | 450000 | 1300 | 260 | 410 | 330 | 815 | 715 | 560 | 10 | 67 | – | 115.6 | 13000 | 1773 |
| 280 300 320 | 470 | 380 | 41 | |||||||||||
| 340 | 550 | 450 | ||||||||||||
| GICL20 | 500000 | 1200 | 280 300 320 | 470 | 380 | 855 | 755 | 595 | 13 | 44 | – | 167.41 | 16000 | 2263 |
| 340 360 | 550 | 450 | ||||||||||||
| GICL21 | 630000 | 1100 | 300 320 | 470 | 380 | 915 | 795 | 611 | 13 | 59 | – | 215.7 | 20000 | 2593 |
| 340 360 380 | 550 | 450 | 44 | |||||||||||
| GICL22 | 710000 | 950 | 340,360,380 | 550 | 450 | 960 | 840 | 632 | 13 | 44 | – | 278.07 | 26000 | 3036 |
| 400 | 650 | 450 | ||||||||||||
| GICL23 | 800000 | 900 | 360,380 | 550 | 450 | 1010 | 890 | 666 | 13 | 44 | – | 379.4 | 29000 | 3668 |
| 400,420 | 650 | 540 | 48 | |||||||||||
| GICL24 | 1000000 | 875 | 380 | 550 | 450 | 1050 | 925 | 685 | 15 | 46 | – | 448.1 | 32000 | 3946 |
| 400,420,450 | 650 | 540 | 50 | |||||||||||
| GICL25 | 1120000 | 850 | 400,420,450,480 | 650 | 540 | 1120 | 970 | 724 | 15 | 50 | – | 564.64 | 34000 | 4443 |
| GICL26 | 1250000 | 825 | 420,450,480,500 | 650 | 540 | 1160 | 990 | 733 | 15 | 50 | – | 637.4 | 37000 | 4791 |
| GICL27 | 1400000 | 800 | 450,480,500 | 650 | 540 | 1210 | 1060 | 739 | 15 | 50 | – | 866.26 | 45000 | 5758 |
| 530 | 800 | 680 | ||||||||||||
| GICL28 | 1600000 | 770 | 480,500 | 650 | 540 | 1250 | 1080 | 805 | 20 | 55 | – | 1020.76 | 47000 | 6232 |
| 530,560 | 800 | 680 | ||||||||||||
| GICL29 | 2240000 | 725 | 500 | 650 | 540 | 1340 | 1200 | 798 | 20 | 57 | – | 1450.84 | 50000 | 7549 |
| 530,560,600 | 800 | 680 | ||||||||||||
| GICL30 | 2800000 | 700 | 530,560,600,630 | 800 | 680 | 1390 | 1240 | 806 | 20 | 55 | – | 1974.17 | 59000 | 9514 |
|
/ Set | |
10 Sets (Min. Order) |
###
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | as Your Requirement |
| Torque: | as Your Requirement |
| Bore Diameter: | as Your Requirement |
| Speed: | 3200~7100 |
| Structure: | Flexible |
###
| Customization: |
|---|
###
| Model | Nominal Torque Tn/N.m |
Speed [n] r/min |
Shaft Hole Dia | Shaft Hole Length |
D | D1 | A | C | C1 | C2 | Rotational InertiaKg |
Grease ml |
Weight Kg |
|
| Y | Z1,J1 | |||||||||||||
| d1,d2,d3 | L | |||||||||||||
| GICL1 | 630 | 7100 | 16,18,19 | 42 | – | 125 | 95 | 75 | 20 | – | – | 0.009 | 55 | 5.9 |
| 20,22,24 | 52 | 38 | – | 24 | ||||||||||
| 25,28 | 62 | 44 | 10 | – | 19 | |||||||||
| 30,32,35,38 | 82 | 60 | 2.5 | 15 | 22 | |||||||||
| GICL2 | 1120 | 6300 | 25,28 | 62 | 44 | 144 | 120 | 88 | 10.5 | – | 29 | 0.02 | 100 | 9.7 |
| 30,32,35,38 | 82 | 60 | 12.5 | 30 | ||||||||||
| 40,42,45,48 | 112 | 84 | 2.5 | 13.5 | 28 | |||||||||
| GICL3 | 2240 | 5900 | 30,32,35,38 | 82 | 60 | 174 | 140 | 106 | 3 | 24.5 | 25 | 0.047 | 140 | 17.2 |
| 40,42,45,48,50,55,56 | 112 | 84 | 17 | 28 | ||||||||||
| 60 | 142 | 107 | 35 | |||||||||||
| GICL4 | 3600 | 5400 | 32,35,38 | 82 | 60 | 196 | 165 | 125.5 | 14 | 37 | 32 | 0.091 | 170 | 24.9 |
| 40,42,45,48,50,55,56 | 112 | 84 | 28 | |||||||||||
| 60,63,65,70 | 142 | 107 | 3 | 17 | 35 | |||||||||
| GICL5 | 5000 | 5000 | 40,42,45,48,50,55,56 | 112 | 84 | 224 | 183 | 142 | 3 | 25 | 28 | 0.167 | 270 | 38 |
| 60 63 65 70 71 75 | 142 | 107 | 20 | 35 | ||||||||||
| 80 | 172 | 132 | 22 | 43 | ||||||||||
| GICL6 | 7100 | 4800 | 48 50 55 56 | 112 | 84 | 241 | 200 | 160 | 6 | 35 | 35 | 0.267 | 380 | 48.2 |
| 60 63 65 70 71 75 | 142 | 107 | 20 | 35 | ||||||||||
| 80 85 90 | 172 | 132 | 4 | 22 | 43 | |||||||||
| GICL7 | 10000 | 4500 | 60 63 65 70 71 75 | 142 | 107 | 260 | 230 | 180 | 4 | 35 | 35 | 0.453 | 570 | 68.9 |
| 80 85 90 95 | 172 | 132 | 22 | 43 | ||||||||||
| 100 | 212 | 167 | 48 | |||||||||||
| GICL8 | 14000 | 4000 | 65 70 71 75 | 142 | 107 | 282 | 245 | 193 | 5 | 35 | 35 | 0.646 | 660 | 83.3 |
| 80 85 90 95 | 172 | 132 | 22 | 43 | ||||||||||
| 100 110 | 212 | 167 | 48 | |||||||||||
| GICL9 | 18000 | 3500 | 70 71 75 | 142 | 107 | 314 | 270 | 208 | 10 | 45 | 45 | 1.036 | 700 | 110 |
| 80 85 90 95 | 172 | 132 | ||||||||||||
| 100 110 120 125 | 212 | 167 | 5 | 22 | 43 | |||||||||
| 49 | ||||||||||||||
| GICL10 | 31500 | 3200 | 80 85 90 95 | 172 | 132 | 346 | 300 | 249 | 5 | 43 | 43 | 1.88 | 900 | 157 |
| 100 110 120 125 | 212 | 167 | 22 | 49 | ||||||||||
| 130 140 | 252 | 202 | 29 | 54 | ||||||||||
| GICL11 | 40000 | 3000 | 100 110 120 125 | 212 | 167 | 380 | 330 | 267 | 6 | 29 | 49 | 3.28 | 1200 | 217 |
| 130 140 150 | 252 | 202 | 54 | |||||||||||
| 160 | 302 | 242 | 64 | |||||||||||
| GICL12 | 56000 | 2600 | 120 125 | 212 | 167 | 442 | 380 | 313 | 6 | 57 | 57 | 5.08 | 2000 | 305 |
| 130 140 150 | 252 | 202 | 29 | 55 | ||||||||||
| 160 170 180 | 302 | 242 | 68 | |||||||||||
| GICL13 | 80000 | 2300 | 140 150 | 252 | 202 | 482 | 420 | 364 | 7 | 54 | 57 | 10.06 | 3000 | 419 |
| 160 170 180 | 302 | 242 | 32 | 70 | ||||||||||
| 190 200 | 352 | 282 | 80 | |||||||||||
| GICL14 | 112000 | 2100 | 160 170 180 | 302 | 242 | 520 | 465 | 415 | 8 | 42 | 70 | 16.774 | 4500 | 594 |
| 190 200 220 | 352 | 282 | 32 | 80 | ||||||||||
| GICL15 | 160000 | 1900 | 190 200 220 | 352 | 282 | 580 | 510 | 429 | 10 | 34 | 80 | 26.55 | 5000 | 783 |
| 140 150 | 410 | 330 | 38 | – | ||||||||||
| GICL16 | 250000 | 1600 | 200 220 | 352 | 282 | 680 | 595 | 501 | 10 | 58 | 80 | 52.22 | 8000 | 1134 |
| 240 250 260 | 410 | 330 | 38 | – | ||||||||||
| 280 | 470 | 380 | 38 | |||||||||||
| GICL17 | 280000 | 1500 | 220 | 352 | 282 | 720 | 645 | 512 | 10 | 74 | 80 | 69 | 10000 | 1305 |
| 240 250 260 | 410 | 330 | ||||||||||||
| 280 300 | 470 | 380 | 39 | – | ||||||||||
| GICL18 | 355000 | 1400 | 240 250 260 | 410 | 330 | 775 | 675 | 524 | 10 | 46 | – | 96.16 | 11000 | 1626 |
| 280 300 320 | 470 | 380 | 41 | – | ||||||||||
| GICL19 | 450000 | 1300 | 260 | 410 | 330 | 815 | 715 | 560 | 10 | 67 | – | 115.6 | 13000 | 1773 |
| 280 300 320 | 470 | 380 | 41 | |||||||||||
| 340 | 550 | 450 | ||||||||||||
| GICL20 | 500000 | 1200 | 280 300 320 | 470 | 380 | 855 | 755 | 595 | 13 | 44 | – | 167.41 | 16000 | 2263 |
| 340 360 | 550 | 450 | ||||||||||||
| GICL21 | 630000 | 1100 | 300 320 | 470 | 380 | 915 | 795 | 611 | 13 | 59 | – | 215.7 | 20000 | 2593 |
| 340 360 380 | 550 | 450 | 44 | |||||||||||
| GICL22 | 710000 | 950 | 340,360,380 | 550 | 450 | 960 | 840 | 632 | 13 | 44 | – | 278.07 | 26000 | 3036 |
| 400 | 650 | 450 | ||||||||||||
| GICL23 | 800000 | 900 | 360,380 | 550 | 450 | 1010 | 890 | 666 | 13 | 44 | – | 379.4 | 29000 | 3668 |
| 400,420 | 650 | 540 | 48 | |||||||||||
| GICL24 | 1000000 | 875 | 380 | 550 | 450 | 1050 | 925 | 685 | 15 | 46 | – | 448.1 | 32000 | 3946 |
| 400,420,450 | 650 | 540 | 50 | |||||||||||
| GICL25 | 1120000 | 850 | 400,420,450,480 | 650 | 540 | 1120 | 970 | 724 | 15 | 50 | – | 564.64 | 34000 | 4443 |
| GICL26 | 1250000 | 825 | 420,450,480,500 | 650 | 540 | 1160 | 990 | 733 | 15 | 50 | – | 637.4 | 37000 | 4791 |
| GICL27 | 1400000 | 800 | 450,480,500 | 650 | 540 | 1210 | 1060 | 739 | 15 | 50 | – | 866.26 | 45000 | 5758 |
| 530 | 800 | 680 | ||||||||||||
| GICL28 | 1600000 | 770 | 480,500 | 650 | 540 | 1250 | 1080 | 805 | 20 | 55 | – | 1020.76 | 47000 | 6232 |
| 530,560 | 800 | 680 | ||||||||||||
| GICL29 | 2240000 | 725 | 500 | 650 | 540 | 1340 | 1200 | 798 | 20 | 57 | – | 1450.84 | 50000 | 7549 |
| 530,560,600 | 800 | 680 | ||||||||||||
| GICL30 | 2800000 | 700 | 530,560,600,630 | 800 | 680 | 1390 | 1240 | 806 | 20 | 55 | – | 1974.17 | 59000 | 9514 |
Types of Couplings
A coupling is a device used to join two shafts together and transmit power. Its purpose is to join rotating equipment while permitting a degree of end movement and misalignment. There are many types of couplings, and it is important to choose the right one for your application. Here are a few examples of couplings.
Mechanical
The mechanical coupling is an important component in power transmission systems. These couplings come in various forms and can be used in different types of applications. They can be flexible or rigid and operate in compression or shear. In some cases, they are permanently attached to the shaft, while in other cases, they are removable for service.
The simplest type of mechanical coupling is the sleeve coupling. It consists of a cylindrical sleeve with an internal diameter equal to the diameter of the shafts. The sleeve is connected to the shafts by a key that restricts their relative motion and prevents slippage. A few sleeve couplings also have threaded holes to prevent axial movement. This type of coupling is typically used for medium to light-duty torque.
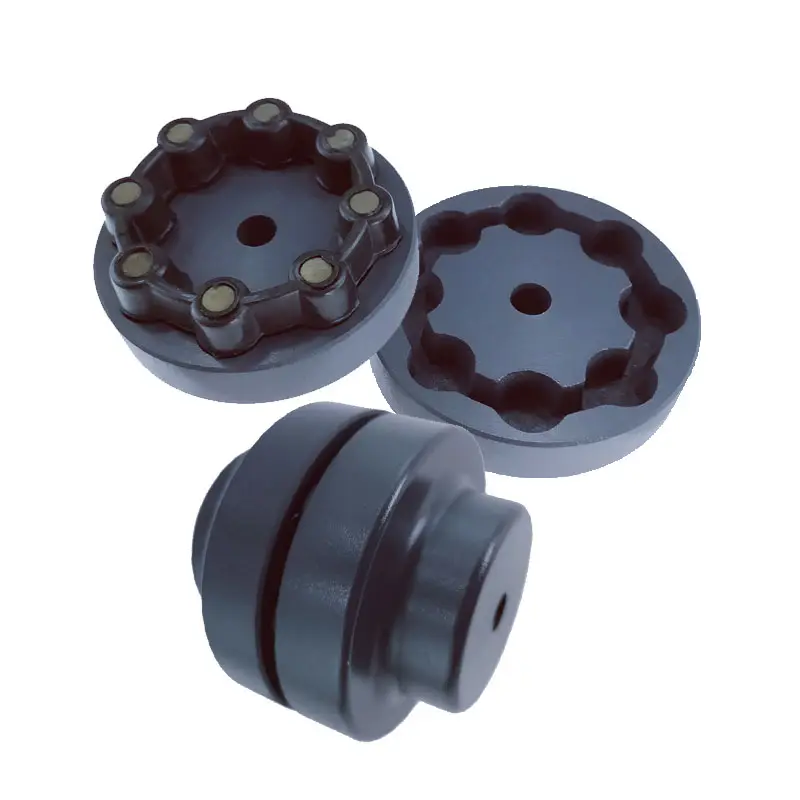
Another type of mechanical coupling is a jaw coupling. It is used in motion control and general low-power transmission applications. This type of coupling does not require lubrication and is capable of accommodating angular misalignment. Unlike other types of couplings, the jaw coupling uses two hubs with intermeshing jaws. The jaw coupling’s spider is typically made of copper alloys. In addition, it is suitable for shock and vibration loads.
Mechanical couplings can be made from a variety of materials. One popular choice is rubber. The material can be natural or chloroprene. These materials are flexible and can tolerate slight misalignment.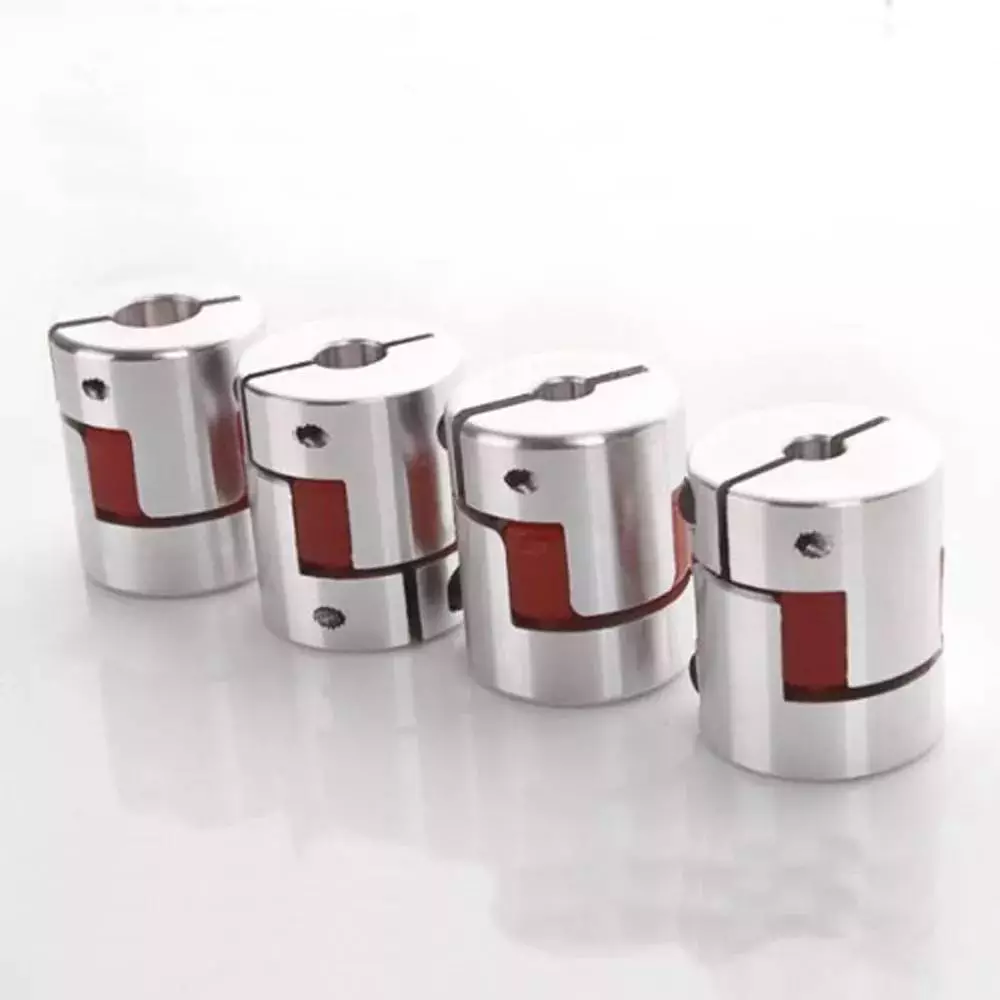
Electrical
Electrical coupling is the process in which a single electrical signal is transferred from a nerve cell to another. It occurs when electrical signals from two nerve cells interact with each other in a way similar to haptic transmission. This type of coupling can occur on its own or in combination with electrotonic coupling in gap junctions.
Electrical coupling is often associated with oscillatory behavior of neurons. The mechanism of electrical coupling is complex and is studied mathematically to understand its effect on oscillatory neuron networks. For example, electrical coupling can increase or decrease the frequency of an oscillator, depending on the state of the neuron coupled to it.
The site of coupling is usually the junction of opposing cell membranes. The cellular resistance and the coupling resistance are measured in voltage-clamp experiments. This type of coupling has a specific resistance of 100 O-cm. As a result, the coupling resistance varies with the frequency.
The authors of this study noted that electrotonic coupling depends on the ratio between the resistance of the nonjunctional membranes and the junctional membranes. The voltage attenuation technique helps reveal the differences in resistance and shunting through the intercellular medium. However, it is unclear whether electrotonic coupling is electrostatically mediated.
Electrical coupling has also been suggested to play a role in the intercellular transfer of information. There are many examples that support this theory. A message can be a distinct qualitative or quantitative signal, which results in a gradient in the cells. Although gap junctions are absent at many embryonic interaction sites, increasing evidence suggests a role in information transfer.
Flexible
When it comes to choosing the right Flexible Coupling, there are several factors that you should take into account. Among these factors is the backlash that can be caused by the movement of the coupling. The reason for this problem is the fact that couplings that do not have anti-fungal properties can be easily infected by mold. The best way to avoid this is to pay attention to the moisture content of the area where you are installing the coupling. By following these guidelines, you can ensure the best possible installation.
To ensure that you are getting the most out of your flexible couplings, you must consider their characteristics and how easy they are to install, assemble, and maintain. You should also look for elements that are field-replaceable. Another important factor is the coupling’s torsional rigidity. It should also be able to handle reactionary loads caused by misalignment.
Flexible couplings come in many different types. There are diaphragm and spiral couplings. These couplings allow for axial motion, angular misalignment, and parallel offset. They have one-piece construction and are made from stainless steel or aluminum. These couplings also offer high torsional stiffness, which is beneficial for applications requiring high torques.
Flexible couplings have several advantages over their rigid counterparts. They are designed to handle misalignments of up to seven degrees and 0.025 inches. These characteristics are important in motion control applications. Flexible couplings are also inexpensive, and they do not require maintenance.
Beam
A beam coupling is a type of mechanical coupling, usually one solid piece, that connects two mechanical parts. Its performance is largely determined by the material used. Typical materials include stainless steel, aluminum, Delrin, and titanium. The beam coupling is rated for different speeds and torques. The coupling should be selected according to the application. In addition to the material, the application should also consider the speed and torque of the system.
There are two main types of beam couplings. The first is the helical beam coupling, which has a continuous multi spiral cut. This type of coupling offers a high degree of flexibility and compensates for a high degree of misalignment. The second type of beam coupling is the helical shaft coupling, which has a low torsional stiffness, which makes it ideal for small torque applications.
Another type of beam coupling is the multiple beam design, which combines two beams. It allows for more tolerance in manufacturing and installation and protects expensive components from excessive bearing loads. It also helps keep beams shorter than a single beam coupling. This type of coupling also enables a higher torque capacity and torsional stiffness.
Beam couplings can be manufactured with different materials, including stainless steel and aluminum. The “A” series is available in aluminum and stainless steel and is ideal for general-purpose and light-duty applications. It is also economical and durable. This type of coupling can also be used with low torque pumps or encoder/resolver systems.
Pin & bush
The Pin & bush coupling is a versatile, general-purpose coupling with high tensile bolts and rubber bushes. It can tolerate a wide range of operating temperatures and is suitable for use in oil and water-resistance applications. Its unique design enables it to be used in either direction. In addition, it requires no lubrication.
The pin bush coupling is a fail-safe coupling with a long service life and is used for high-torque applications. It provides torsional flexibility and dampens shocks, making it a flexible coupling that protects equipment and reduces maintenance costs. Its hubs are forged from graded cast iron for strength and durability. Besides, the coupling’s elastomer elements reduce vibration and impact loads. It also accommodates a misalignment of up to 0.5 degrees.
Pin & bush couplings are a popular choice for a variety of different applications. This coupling features a protective flange design that protects the coupling flange from wear and tear. The coupling nut is secured to one flange, while a rubber or leather bush sits between the other flange. Its unique design makes it ideal for use in applications where misalignment is a small factor. The rubber bushing also helps absorb vibration and shock.
Mesh tooth
Mesh tooth couplings are used to transfer torque between two shafts and reduce backlash. However, mesh tooth couplings have some limitations. One disadvantage is the break-away friction factor in the axial direction. This problem is caused by the high contact force between the tooth and gear mesh. This can cause unpredictable forces on the shafts.
In this paper, we present a FEM model for mesh tooth coupling. We first validate the mesh density. To do so, we compute the bolt stress as a uniaxial tensile during the tightening process. We used different mesh sizes and mesh density to validate our results.
The mesh stiffness of gear pairs is influenced by lead crown relief and misalignment. For example, if one tooth is positioned too far in the axis, the mesh stiffness will be decreased. A misaligned gear pair will lose torque capacity. A mesh tooth coupling can be lubricated with oil.
An ideal mesh tooth coupling has no gaps between the teeth, which reduces the risk of uneven wear. The coupling’s quality exposed fasteners include SAE Grade 5 bolts. It also offers corrosion resistance. The couplings are compatible with industrial environments. They also eliminate the need for selective assembly in sleeve couplings.

editor by CX 2023-03-27