Product Description
Product Description
Diaphragm couplings provide an economical transmission solution for general equipment, with waisted diaphragms, greater operating torque and less diaphragm stress.
The maximum opening value is a round hole or a tapered hole with a keyway. If you need to open other types of holes, please consult CZPT Technology.
Related Products
Main application:
DWZ disc eddy current brake is mainly used as load in loading dynamometer equipment. it is experimental apparatus which can measure the dynamic mechanical properties, especially in dynamic loading test whose power value is small or tiny, also can be treated as suction power devices of other dynamic devices.
DW series disc eddy current dynamometer is, is that add device for measuring torque and rotational speed on DWZ series disc eddy current brake, it is experimental apparatus which can measure the dynamic mechnical properties, especial in dynamic loading test whose power value is small or tiny.
CW eddy current brake as a load is mainly used to measure the mechanical characteristics of inspection equipment, it and other control instrument (including loading apparatus, torque speed sensor and torque power acquisition instrument etc.) can be composed of eddy current dynamometer can be used for performance testing of the internal combustion engine, motor, gas turbine, automobile and its dynamic mechanical components, compared with other power measuring device, the CW series power measuring device has the advantages of reliability, high stability and practicability.
| Eddy current brake/dynamometer | Rated Power | Rated torque | Rated speed | Maximum rotational speed | Turning inertia | Maximum excitation voltage | Maximum excitation Current | Cooling water pressure | Flow of the cooling water |
| DWZ/DW-0.75 | 0.75 | 5 | 2000-2600 | 16000 | 0.002 | 80 | 3 | 0.1~0.3 | 1 |
| DWZ/DW-3 | 3 | 10 | 2000-2600 | 14000 | 0.003 | 80 | 3 | 0.1~0.3 | 2 |
| DWZ/DW-6 | 6 | 25 | 2000-2600 | 14000 | 0.003 | 80 | 3 | 0.1~0.3 | 3 |
| DWZ/DW-10 | 10 | 50 | 2000-2600 | 13000 | 0.01 | 80 | 3 | 0.1~0.3 | 4.5 |
| DWZ/DW-16 | 16 | 70 | 2000-2600 | 13000 | 0.02 | 80 | 3.5 | 0.1~0.3 | 6.5 |
| DWZ/DW-25 | 25 | 120 | 2000-2600 | 11000 | 0.05 | 80 | 3.5 | 0.1~0.3 | 15 |
| DWZ/DW-40 | 40 | 160 | 2000-2600 | 10000 | 0.1 | 90 | 4 | 0.1~0.3 | 25 |
| DWZ/DW-63 | 63 | 250 | 2000-2600 | 9000 | 0.18 | 90 | 4 | 0.1~0.3 | 45 |
| DWZ/DW-100 | 100 | 400 | 2000-2600 | 8500 | 0.32 | 120 | 4 | 0.1~0.3 | 60 |
| DWZ/DW-160 | 160 | 600 | 2000-2600 | 8000 | 0.52 | 120 | 5 | 0.1~0.3 | 100 |
| DWZ/DW-250 | 250 | 1100 | 2000-2600 | 7000 | 1.8 | 150 | 5 | 0.2~0.4 | 180 |
| DWZ/DW-300 | 300 | 1600 | 2000-2600 | 6000 | 2.7 | 150 | 5 | 0.2~0.4 | 210 |
| DWZ/DW-400 | 400 | 2200 | 2000-2600 | 5000 | 3.6 | 180 | 10 | 0.2~0.4 | 300 |
| DWZ/DW-630 | 630 | 3600 | 2000-2600 | 5000 | 5.3 | 180 | 10 | 0.2~0.4 | 450 |
Company Information:
Product Line:
Advantages:
FAQ:
CONTACT US:
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Nonstandard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 19-32 |
| Torque: | 70-80N.M |
| Bore Diameter: | 19mm |
| Speed: | 10000r/M |
| Structure: | Flexible |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Types of Couplings
A coupling is a device that connects two shafts and transmits power from one to the other. Its main purpose is to join two pieces of rotating equipment. It also allows for some degree of misalignment or end movement. Here are a few examples of coupling types: Beam coupling, Flexible coupling, Magnetic coupling, and Shaft coupling.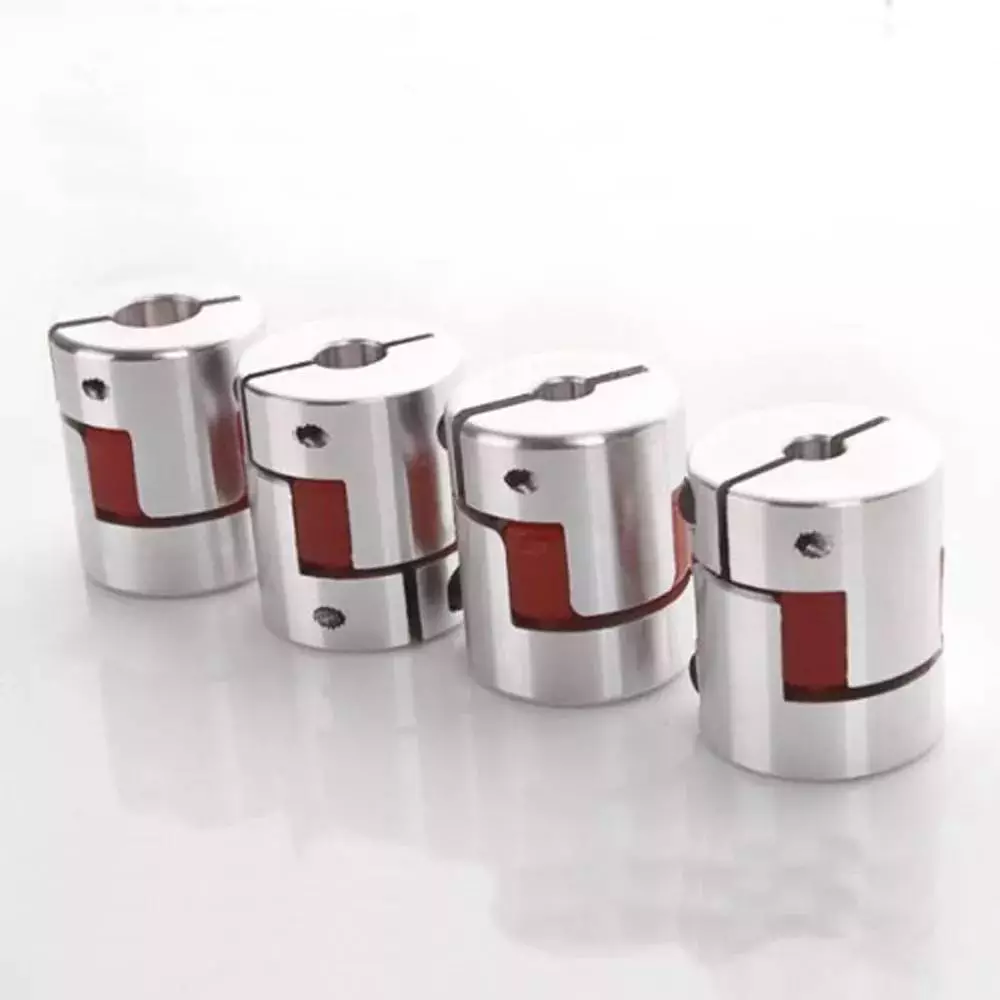
Beam coupling
Beam couplings are used to couple motors and other devices. They are available in several types, including flexible, slit, and rigid beam couplings. Each has unique properties and characteristics. These couplings are best for applications requiring a high level of precision and long life. They are also a practical solution for the connection of stepping and servo motors with screw rods.
Beam couplings are usually made of stainless steel or aluminum alloy, and feature spiral and parallel cut designs. Multiple cuts allow the coupling to accommodate multiple beams and improve angular and parallel misalignment tolerances. Additionally, beam couplings are comparatively cheaper than other types of rotary joints, and they require minimal maintenance.
The materials of a beam coupling should be considered early in the specification process. They are typically made of aluminum or stainless steel, but they can also be manufactured from Delrin, titanium, and other engineering grade materials. Beam couplings are often available in multiple sizes to fit specific shaft diameters.
Beam couplings are a key component of motion control systems. They provide excellent characteristics when used properly, and they are a popular choice for many applications. A thorough understanding of each type of coupling will help to prevent coupling failure and enhance system performance. Therefore, it is important to choose the right coupling for your application.
Various types of beam couplings have unique advantages and disadvantages. The FCR/FSR design has two sets of three beams. It is available in both metric and inch shaft sizes. The FCR/FSR couplings are ideal for light-duty power transmission applications. A metric shaft is more suitable for these applications, while an inch shaft is preferred for heavier duty applications.
Two types of beam couplings are available from Ruland. The Ruland Flexible beam coupling has a multi-helical cut design that offers a greater flexibility than commodity beam couplings. This design allows for higher torque capabilities while minimizing wind-up. In addition, it is also more durable than its commodity counterparts.
Flexible coupling
A flexible coupling is a versatile mechanical connection that allows for the easy coupling of two moving parts. The design of these couplings allows for a variety of stiffness levels and can address a variety of problems, such as torsional vibrations or critical speed. However, there are a number of tradeoffs associated with flexible couplings.
One of the biggest issues is the installation of the coupling, which requires stretching. This problem can be exacerbated by cold temperatures. In such a case, it is vital to install the coupling properly. Using a gear clamp is one of the most important steps in a successful installation. A gear clamp will keep the coupling in place and prevent it from leaking.
Another common type of flexible coupling is the gear coupling. These couplings are composed of two hubs with crowned external gear teeth that mesh with two internally splined flanged sleeves. The massive size of the teeth makes them resemble gears. Gear couplings offer good torque characteristics but require periodic lubrication. These couplings can also be expensive and have a limited number of applications.
Another type of flexible coupling is the SDP/SI helical coupling. These couplings can accommodate axial motion, angular misalignment, and parallel offset. This design incorporates a spiral pattern that makes them flexible. These couplings are available in stainless steel and aluminum.
A flexible coupling has a wide range of applications. Generally, it is used to connect two rotating pieces of equipment. Depending on its design, it can be used to join two pieces of machinery that move in different directions. This type of coupling is a type of elastomeric coupling, which has elastic properties.
There are many types of flexible couplings available for different types of applications. The purpose of a flexible coupling is to transmit rotational power from one shaft to another. It is also useful for transmitting torque. However, it is important to note that not all flexible couplings are created equally. Make sure to use a reputable brand for your coupling needs. It will ensure a reliable connection.
The simplest and most commonly used type of flexible coupling is the grid coupling. This type of coupling uses two hubs with slotted surfaces. The steel grid is allowed to slide along these slots, which gives it the ability to flex. The only limitation of this type of coupling is that it can only tolerate a 1/3 degree misalignment. It can transmit torques up to 3,656 Nm.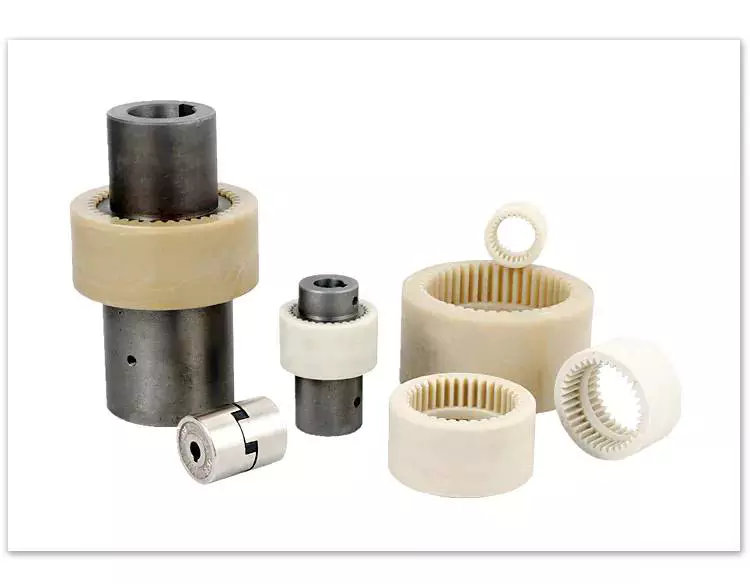
Magnetic coupling
Magnetic coupling is a technique used to transfer torque from one shaft to another using a magnetic field. It is the most common type of coupling used in machinery. It is highly effective when transferring torque from a rotating motor to a rotating shaft. Magnetic couplings can handle high torques and high speeds.
Magnetic coupling is described by the energy difference between a high-spin state and a broken symmetry state, with the former being the energy of a true singlet state. In single-determinant theories, this energy difference is called the Kij. Usually, the broken-symmetry state is a state with two interacting local high-spin centers.
The magnetic coupling device is regarded as a qualitative leap in the reaction still industry. It has solved a number of problems that had plagued the industry, including flammability, explosiveness, and leakage. Magnetic couplings are a great solution for many applications. The chemical and pharmaceutical industries use them for various processes, including reaction stills.
Magnetic couplings are a good choice for harsh environments and for tight spaces. Their enclosed design keeps them fluid and dust-proof. They are also corrosion-resistant. In addition, magnetic couplings are more affordable than mechanical couplings, especially in areas where access is restricted. They are also popular for testing and temporary installations.
Another use for magnetic coupling is in touch screens. While touch screens use capacitive and resistive elements, magnetic coupling has found a cool new application in wireless charging. While the finger tracking on touch screens may seem like a boley job, the process is very sensitive. The devices that use wireless charging need to have very large coils that are locked into resonant magnetic coupling.
Magnetic couplings also help reduce hydraulic horsepower. They cushion starts and reduce alignment problems. They can also improve flow in oversized pumps. A magnetic coupling with an 8 percent air gap can reduce hydraulic HP by approximately 27 percent. In addition, they can be used in aggressive environments. They also help reduce repair costs.
Magnetic couplings are a great choice for pumps and propeller systems because they have the added advantage of being watertight and preventing shaft failure. These systems also have the benefit of not requiring rotating seals.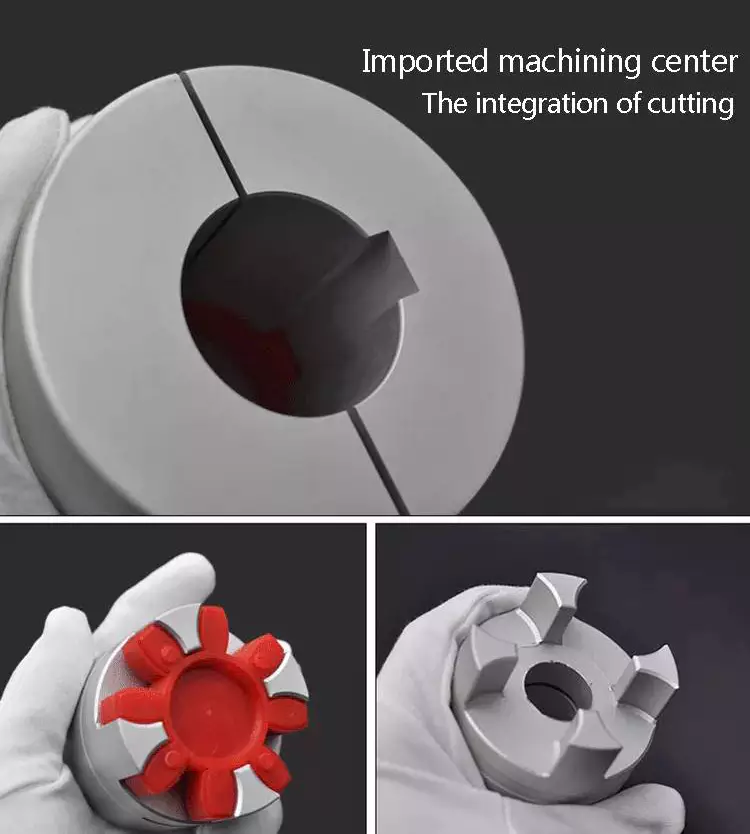
Shaft coupling
A shaft coupling joins two shafts and transmits rotational motion. Generally, shaft couplings allow for some degree of misalignment, but there are also torque limiters. Selecting the right coupling can save you time and money and prevent equipment downtime. Here are the main features to consider when purchasing a coupling for your application.
Shaft couplings should be easy to install and disassemble, transmit full power to the mated shaft, and reduce shock loads. A shaft coupling that does not have projecting parts should be used for machines that move or rotate at high speeds. Some types of shaft couplings are flexible while others are rigid.
Shaft couplings can be used in a variety of applications, including piping systems. They can be used to connect shafts that are misaligned and help maintain alignment. They can also be used for vibration dampening. Shaft couplings also allow shafts to be disconnected when necessary.
Shaft couplings can accommodate a certain amount of backlash, but this backlash must be well within the tolerance set by the system. Extremely high backlash can break the coupling and cause excessive wear and stress. In addition, excessive backlash can lead to erratic alignment readings. To avoid these issues, operators must reduce backlash to less than 2deg.
Shaft couplings are often referred to by different names. Some are referred to as “sliced” couplings while others are known as “slit” couplings. Both types offer high torque and torsional stiffness. These couplings are typically made from metals with various alloys, such as acetal, stainless steel, or titanium.
CZPT Pulley produces shaft couplings for a variety of applications. These products are used in high-power transmission systems. They have several advantages over friction couplings. In addition to minimizing wear, they don’t require lubrication. They are also capable of transmitting high torque and high speeds.
Another type of shaft coupling is the universal coupling. It is used to transmit power to multiple machines with different spindles. Its keyed receiving side and flanges allow it to transmit power from one machine to another.

editor by CX 2023-07-07
China Flexible Aluminum Double Diaphragm Coupling for Servo Motor Stepping Motor coupling beam
Solution Description
Merchandise Description
Double Diaphragm Coupling for Servo Motor
Function
>High torque rigidity, can correctly control the rotation of the shaft, can carry out large-precision control
>Designed for servo and stepping motor
>No hole in between the shaft and sleeve link, common for optimistic and damaging rotation
>Low inertia, suited for higher velocity operation
>The diaphragm is manufactured of spring steel with superb fatigue resistance
>Fastening method of clamping screw
Packaging & Shipping
Bundle: Wood box/Paper carton
Port: HangZhou/ZheJiang or as request
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
About CZPT since 1984
HangZhou Melchizedek Import & Export Co., Ltd. is a chief manufactur in mechanism field and punching/stamp
ing discipline given that 1984. Our primary solution, NMRV worm equipment velocity reducer and collection helical gearbox, XDR,
XDF, XDK, XDShave achieved the sophisticated technique index of the congeneric European and Janpanese produc
ts, We offer regular gears, sprockets, chains, pulleys, couplings, bushes and so on. We also can take orders
of non-common goods, such as gears, shafts, punching components ect, according to customers’ Drawings or sam-
ples.
Our firm has full established of gear including CNC, lathes, milling devices, gear hobbing equipment, g-
ear grinding equipment, equipment honing equipment, gear shaping equipment, worm grinder, grinding equipment, drilling m-
achines, boringmachines, planer, drawing benches, punches, hydraulic presses, plate shearing machines and s-
o on. We have superior tests equipments also.
Our firm has established favorable cooperation relationships with sub-suppliers involving casting, uncooked mat-
erial, heat remedy, surface area finishing and so on.
| To Be Negotiated | 10 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Nonstandard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 10-32 |
| Torque: | >80N.M |
| Bore Diameter: | 9mm |
| Speed: | 10000r/M |
| Structure: | Flexible |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
| To Be Negotiated | 10 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Nonstandard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 10-32 |
| Torque: | >80N.M |
| Bore Diameter: | 9mm |
| Speed: | 10000r/M |
| Structure: | Flexible |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
Programming With Couplings
A coupling is a mechanical device that connects two shafts together and transmits power. Its purpose is to join rotating equipment and allows some degree of end-movement or misalignment. There are many different types of couplings. It’s important to choose the right one for your application.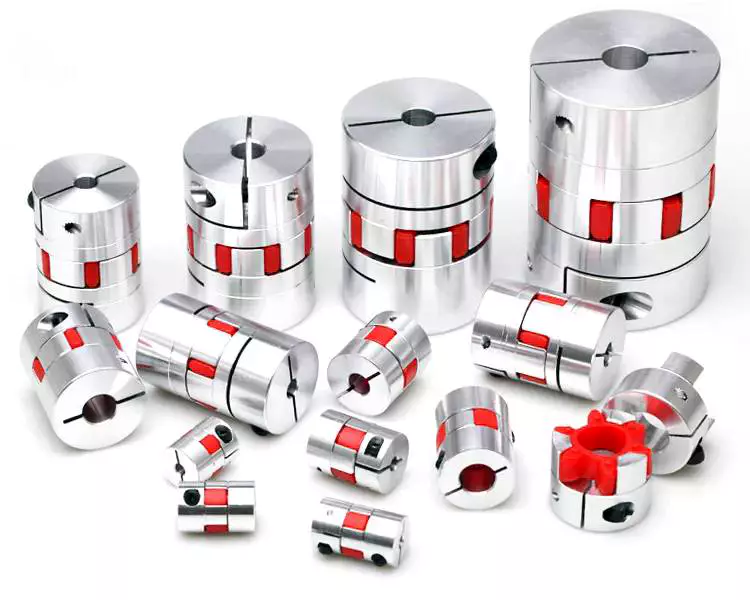
Mechanical connection between two shafts
There are many ways to achieve mechanical connection between two shafts, including the use of a coupling. One common type is the beam coupling, which is also known as a helical coupling. It is used for transmission of torque between two shafts. This type of connection accommodates axial, parallel and angular misalignments.
The hubs and shafts of a worm gear are connected together by a coupling. This mechanical connection allows one shaft to turn another without causing a mechanical failure. This type of coupling is made from sliding or rubbing parts to transfer torque. However, the coupling is not designed to withstand jerks, so it isn’t suitable for high-speed applications.
The use of a coupling is common in machinery and equipment. It helps transmit power from one drive shaft to the other, while adding mechanical flexibility. It is also useful for reducing the impact and vibration caused by misalignment. It also protects the drive shaft components from wear and tear.
A double-hook coupling can be used to provide a uniform angular velocity at the driven shaft. Another example is a double-jointed coupling. A double-jointed coupling can be used to connect shafts that are not directly intersecting. The double-jointed yoke can be used for the same purpose.
A shaft coupling is a device that maintains a strong mechanical connection between two shafts. It transfers motion from one shaft to another, at all loads and misalignments. Unlike a conventional linkage, a shaft coupling isn’t designed to allow relative motion between the two shafts. Couplings often serve several purposes in a machine, but their primary use is torque and power transmission.
Functions that control the flow of another function
One of the simplest programming constructs is a function that controls the flow of another function. A function can take an argument and return a different value, but it must be ready to return before it can pass that value to another function. To do this, you can use the goto statement and the if statement. Another way to control flow is to use a conditional statement.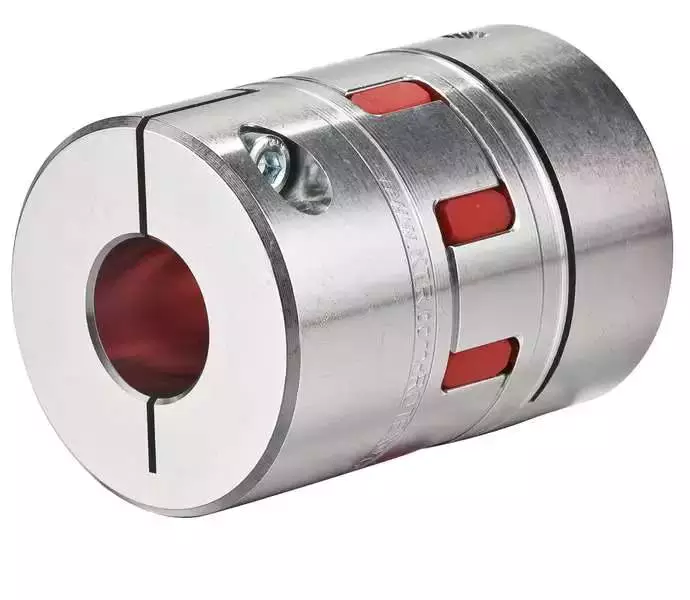
Criteria for selecting a coupling
There are several important factors to consider when choosing the right coupling. One of the most important factors is coupling stiffness, which depends on the material used and the shape. The stiffness of a coupling determines its ability to resist elastic deformation. A stiff coupling is desirable for certain types of applications, but it’s undesirable for others. Stiffness can reduce the performance of a system if there’s too much inertia. To avoid this, ensure that the coupling you choose is within the recommended limits.
The size of a coupling is also important. Different coupling types can accommodate different shaft sizes and shapes. Some couplings have special features, such as braking and shear pin protection. When choosing a coupling, you should also consider the type of driven equipment. If you need to connect a high-torque motor, for example, you’ll want to choose a gear coupling. Likewise, a high-speed machine may require a disc coupling.
Another factor to consider when selecting a coupling is the torque rating. Despite its importance, it’s often underestimated. The torque rating is defined as the torque of the coupling divided by its OD. In some cases, torque may fluctuate during a cycle, requiring a coupling with a higher torque rating.
Torsionally flexible couplings are also important to consider. Their design should be able to withstand the torque required during operation, as well as the required speed. The coupling should also have a high degree of torsional stiffness, as well as damping. Furthermore, a damping coupling can reduce the energy wasted through vibration.
The sizing of a coupling is also determined by the torque. Many engineers use torque to select the correct coupling size, but they also take into consideration torsional flexibility and torsional stiffness. For example, a shaft may be able to handle large torque without damaging the coupling, while a disk may be unable to handle large amounts of torque.
Besides torque, another important consideration in coupling selection is the cost. While a coupling may be cheaper, it may be less reliable or easier to maintain. Couplings that are difficult to service may not last as long. They may also require frequent maintenance. If that’s the case, consider purchasing a coupling with a low service factor.
There are many different types of couplings. Some require additional lubrication throughout their lifetime, while others are 100% lubrication-free. An example of a 100% lubrication-free coupling is the RBI flexible coupling from CZPT. This type of coupling can significantly reduce your total cost of ownership.
In addition to the above-mentioned benefits, elastomeric couplings are low-cost and need little maintenance. While they are often cheaper than metallic couplings, they also have excellent shock absorption and vibration dampening properties. However, they are susceptible to high temperatures. Also, they are difficult to balance as an assembly, and have limited overload torque capacity.

editor by czh 2023-01-07
China Disc Couplings Torsionally Rigid Double Disc Packs with Spacer Diaphragm Coupling coupling agent
Merchandise Description
Disc Couplings Torsionally Rigid Double Disc Packs with Spacer Diaphragm Coupling
Merchandise Description
1. Applies to flexibly push shaft, permitting a more significant axial radial displacement and displacement.
two. It Has a easy framework and simple servicing.
three. Disassembly is simple.
4. low sounds.
5. Transmission performance loss, prolonged beneficial functioning existence.
Product Parameters
| Size | Torque Tn/N.m |
Speed (rmin) |
Weight/kg | Moment of inertia g cm’ |
Main measurement/mm | Allowable compensation | |||||||
| d | D | A | B | L | C | Axial | Angular | Radial | |||||
| 00 | 9.8 | 20000 | .23 | three | 3-20 | fifty seven | four.9 | twenty | 100 | 60 | ±1.6 | 2° | .5 |
| 01 | 33 | 20000 | 1.two | eight | five-22 | sixty eight | six.1 | 26 | 141 | 89 | ±1.6 | 2° | .5 |
| 02 | 90 | 20000 | 1.9 | 24 | 6-32 | 81 | 6.6 | 26 | 141 | 89 | ±1.6 | 2° | .5 |
| 03 | 173 | 18000 | 2.nine | forty eight | eight-35 | 93 | eight.4 | 29 | one hundred sixty | 102 | ±2.four | 2° | .6 |
| 04 | 245 | 15000 | four.7 | 80 | ten-42 | 104 | eleven.2 | 34 | 195 | 127 | ±2.eight | 2° | .7 |
| 05 | 420 | 13000 | seven.1 | 224 | 15-fifty | 126 | eleven.7 | 42 | 211 | 127 | ±3.2 | 1°30″ | .7 |
| 06 | 772 | 12000 | ten.eight | 400 | 20-sixty | 143 | eleven.7 | 48 | 223 | 127 | ±3.six | 1°30″ | .8 |
| 07 | 1270 | ten thousand | 16.3 | 1080 | 25-75 | 168 | 16.8 | fifty eight | 243 | 127 | ±4. | 1°30″ | .8 |
| 08 | 2080 | 10000 | 24.7 | 2080 | 30-82 | 194 | seventeen.0 | sixty four | 268 | one hundred forty | ±4.4 | 1°30″ | .9 |
| 09 | 3328 | 9000 | 32.5 | 3520 | thirty-95 | 214 | 21.6 | seventy seven | 306 | 152 | ±4.8 | 1°30″ | .9 |
| 10 | 4900 | 8000 | 50 | 7200 | ten-108 | 246 | 23.9 | 89 | 356 | 178 | ±5.two | 1°30″ | one.0 |
| 11 | 6368 | 6300 | seventy five | 12800 | fifty two-118 | 276 | 27.2 | 102 | 382 | 178 | ±5.six | 1°30″ | one.2 |
| 12 | 8900 | 6300 | 72.2 | 18000 | sixty-a hundred and ten | 276 | seventeen.5 | 128 | 409 | 153 | ±3.six | one” | 1.2 |
| thirteen | 15280 | 5000 | one hundred twenty | 37000 | 60-one hundred thirty five | 308 | 19.0 | 160 | 492 | 172 | ±4. | 1″ | 1.2 |
| 14 | 25410 | 4700 | a hundred seventy five | 68000 | sixty-155 | 346 | 21.5 | 182 | 554 | one hundred ninety | ±4. | one” | one.2 |
| 15 | 37130 | 4300 | 234 | 108000 | sixty-a hundred sixty five | 375 | 24.0 | 198 | 620 | 224 | ±4. | one” | one.3 |
| sixteen | 47120 | 3900 | 306 | 167000 | 70-one hundred eighty | 410 | 29.5 | 214 | 682 | 254 | ±4.four | 1″ | one.3 |
| seventeen | 57000 | 3500 | 369 | 250000 | 70-a hundred ninety | 445 | 29.5 | 225 | 720 | 270 | ±4.four | one” | one.4 |
| 18 | 63186 | 3500 | 448 | 311000 | 80-205 | 470 | 31.0 | 248 | 770 | 274 | ±4.8 | one” | one.5 |
| 19 | 82590 | 3200 | 596 | 480000 | ninety-230 | 512 | 32.0 | 278 | 843 | 287 | ±4.eight | one” | one.6 |
| 20 | 157100 | 2800 | 763 | 747000 | ninety-255 | 556 | 32.5 | 305 | 902 | 292 | ±5.two | one” | 1.8 |
| 21 | 126070 | 2450 | 919 | 1016000 | 100-265 | 588 | 34.0 | 318 | 948 | 312 | ±5.4 | 1″ | one.8 |
| 22 | 146350 | 2150 | 1068 | 1386000 | 100-275 | 630 | 34.0 | 332 | 1008 | 344 | ±5.6 | one” | two.0 |
| 23 | 173830 | 2000 | 1235 | 1784000 | one hundred-290 | 655 | 35.5 | 348 | 1052 | 356 | ±6. | 1″ | 2.0 |
Connected Items
Firm Profile
FAQ
Q: Can you make the coupling with customization?
A: Sure, we can customize for each your ask for.
Q: Do you give samples?
A: Yes. The sample is obtainable for tests.
Q: What is your MOQ?
A: It is 10pcs for the starting of our business.
Q: What is your direct time?
A: Common items need to have 5-30days, a bit longer for custom-made goods.
Q: Do you offer complex assist?
A: Indeed. Our firm has a style and growth group, and we can offer specialized help if you
want.
Q: How to ship to us?
A: It is offered by air, sea, or by teach.
Q: How to spend the income?
A: T/T and L/C are desired, with various currencies, which includes USD, EUR, RMB, etc.
Q: How can I know if the merchandise is suitable for me?
A: >1ST validate drawing and specification >2nd take a look at sample >3rd commence mass creation.
Q: Can I arrive to your firm to visit?
A: Of course, you are welcome to check out us at any time.
Q: How shall we speak to you?
A: You can deliver an inquiry directly, and we will answer inside of 24 several hours.
|
US $15-25 / Piece | |
1,000 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
###
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | Custom |
| Torque: | <10N.M |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) Yellow
|
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Size | Torque Tn/N.m |
Speed (rmin) |
Weight/kg | Moment of inertia g cm’ |
Main size/mm | Allowable compensation | |||||||
| d | D | A | B | L | C | Axial | Angular | Radial | |||||
| 00 | 9.8 | 20000 | 0.23 | 3 | 3-20 | 57 | 4.9 | 20 | 100 | 60 | ±1.6 | 2° | 0.5 |
| 01 | 33 | 20000 | 1.2 | 8 | 5-22 | 68 | 6.1 | 26 | 141 | 89 | ±1.6 | 2° | 0.5 |
| 02 | 90 | 20000 | 1.9 | 24 | 6-32 | 81 | 6.6 | 26 | 141 | 89 | ±1.6 | 2° | 0.5 |
| 03 | 173 | 18000 | 2.9 | 48 | 8-35 | 93 | 8.4 | 29 | 160 | 102 | ±2.4 | 2° | 0.6 |
| 04 | 245 | 15000 | 4.7 | 80 | 10-42 | 104 | 11.2 | 34 | 195 | 127 | ±2.8 | 2° | 0.7 |
| 05 | 420 | 13000 | 7.1 | 224 | 15-50 | 126 | 11.7 | 42 | 211 | 127 | ±3.2 | 1°30" | 0.7 |
| 06 | 772 | 12000 | 10.8 | 400 | 20-60 | 143 | 11.7 | 48 | 223 | 127 | ±3.6 | 1°30" | 0.8 |
| 07 | 1270 | 10000 | 16.3 | 1080 | 25-75 | 168 | 16.8 | 58 | 243 | 127 | ±4.0 | 1°30" | 0.8 |
| 08 | 2080 | 10000 | 24.7 | 2080 | 30-82 | 194 | 17.0 | 64 | 268 | 140 | ±4.4 | 1°30" | 0.9 |
| 09 | 3328 | 9000 | 32.5 | 3520 | 30-95 | 214 | 21.6 | 77 | 306 | 152 | ±4.8 | 1°30" | 0.9 |
| 10 | 4900 | 8000 | 50 | 7200 | 10-108 | 246 | 23.9 | 89 | 356 | 178 | ±5.2 | 1°30" | 1.0 |
| 11 | 6368 | 6300 | 75 | 12800 | 52-118 | 276 | 27.2 | 102 | 382 | 178 | ±5.6 | 1°30" | 1.2 |
| 12 | 8900 | 6300 | 72.2 | 18000 | 60-110 | 276 | 17.5 | 128 | 409 | 153 | ±3.6 | 1" | 1.2 |
| 13 | 15280 | 5000 | 120 | 37000 | 60-135 | 308 | 19.0 | 160 | 492 | 172 | ±4.0 | 1" | 1.2 |
| 14 | 25410 | 4700 | 175 | 68000 | 60-155 | 346 | 21.5 | 182 | 554 | 190 | ±4.0 | 1" | 1.2 |
| 15 | 37130 | 4300 | 234 | 108000 | 60-165 | 375 | 24.0 | 198 | 620 | 224 | ±4.0 | 1" | 1.3 |
| 16 | 47120 | 3900 | 306 | 167000 | 70-180 | 410 | 29.5 | 214 | 682 | 254 | ±4.4 | 1" | 1.3 |
| 17 | 57000 | 3500 | 369 | 250000 | 70-190 | 445 | 29.5 | 225 | 720 | 270 | ±4.4 | 1" | 1.4 |
| 18 | 63186 | 3500 | 448 | 311000 | 80-205 | 470 | 31.0 | 248 | 770 | 274 | ±4.8 | 1" | 1.5 |
| 19 | 82590 | 3200 | 596 | 480000 | 90-230 | 512 | 32.0 | 278 | 843 | 287 | ±4.8 | 1" | 1.6 |
| 20 | 102100 | 2800 | 763 | 747000 | 90-255 | 556 | 32.5 | 305 | 902 | 292 | ±5.2 | 1" | 1.8 |
| 21 | 126070 | 2450 | 919 | 1016000 | 100-265 | 588 | 34.0 | 318 | 948 | 312 | ±5.4 | 1" | 1.8 |
| 22 | 146350 | 2150 | 1068 | 1386000 | 100-275 | 630 | 34.0 | 332 | 1008 | 344 | ±5.6 | 1" | 2.0 |
| 23 | 173830 | 2000 | 1235 | 1784000 | 100-290 | 655 | 35.5 | 348 | 1052 | 356 | ±6.0 | 1" | 2.0 |
|
US $15-25 / Piece | |
1,000 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
###
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | Custom |
| Torque: | <10N.M |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) Yellow
|
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Size | Torque Tn/N.m |
Speed (rmin) |
Weight/kg | Moment of inertia g cm’ |
Main size/mm | Allowable compensation | |||||||
| d | D | A | B | L | C | Axial | Angular | Radial | |||||
| 00 | 9.8 | 20000 | 0.23 | 3 | 3-20 | 57 | 4.9 | 20 | 100 | 60 | ±1.6 | 2° | 0.5 |
| 01 | 33 | 20000 | 1.2 | 8 | 5-22 | 68 | 6.1 | 26 | 141 | 89 | ±1.6 | 2° | 0.5 |
| 02 | 90 | 20000 | 1.9 | 24 | 6-32 | 81 | 6.6 | 26 | 141 | 89 | ±1.6 | 2° | 0.5 |
| 03 | 173 | 18000 | 2.9 | 48 | 8-35 | 93 | 8.4 | 29 | 160 | 102 | ±2.4 | 2° | 0.6 |
| 04 | 245 | 15000 | 4.7 | 80 | 10-42 | 104 | 11.2 | 34 | 195 | 127 | ±2.8 | 2° | 0.7 |
| 05 | 420 | 13000 | 7.1 | 224 | 15-50 | 126 | 11.7 | 42 | 211 | 127 | ±3.2 | 1°30" | 0.7 |
| 06 | 772 | 12000 | 10.8 | 400 | 20-60 | 143 | 11.7 | 48 | 223 | 127 | ±3.6 | 1°30" | 0.8 |
| 07 | 1270 | 10000 | 16.3 | 1080 | 25-75 | 168 | 16.8 | 58 | 243 | 127 | ±4.0 | 1°30" | 0.8 |
| 08 | 2080 | 10000 | 24.7 | 2080 | 30-82 | 194 | 17.0 | 64 | 268 | 140 | ±4.4 | 1°30" | 0.9 |
| 09 | 3328 | 9000 | 32.5 | 3520 | 30-95 | 214 | 21.6 | 77 | 306 | 152 | ±4.8 | 1°30" | 0.9 |
| 10 | 4900 | 8000 | 50 | 7200 | 10-108 | 246 | 23.9 | 89 | 356 | 178 | ±5.2 | 1°30" | 1.0 |
| 11 | 6368 | 6300 | 75 | 12800 | 52-118 | 276 | 27.2 | 102 | 382 | 178 | ±5.6 | 1°30" | 1.2 |
| 12 | 8900 | 6300 | 72.2 | 18000 | 60-110 | 276 | 17.5 | 128 | 409 | 153 | ±3.6 | 1" | 1.2 |
| 13 | 15280 | 5000 | 120 | 37000 | 60-135 | 308 | 19.0 | 160 | 492 | 172 | ±4.0 | 1" | 1.2 |
| 14 | 25410 | 4700 | 175 | 68000 | 60-155 | 346 | 21.5 | 182 | 554 | 190 | ±4.0 | 1" | 1.2 |
| 15 | 37130 | 4300 | 234 | 108000 | 60-165 | 375 | 24.0 | 198 | 620 | 224 | ±4.0 | 1" | 1.3 |
| 16 | 47120 | 3900 | 306 | 167000 | 70-180 | 410 | 29.5 | 214 | 682 | 254 | ±4.4 | 1" | 1.3 |
| 17 | 57000 | 3500 | 369 | 250000 | 70-190 | 445 | 29.5 | 225 | 720 | 270 | ±4.4 | 1" | 1.4 |
| 18 | 63186 | 3500 | 448 | 311000 | 80-205 | 470 | 31.0 | 248 | 770 | 274 | ±4.8 | 1" | 1.5 |
| 19 | 82590 | 3200 | 596 | 480000 | 90-230 | 512 | 32.0 | 278 | 843 | 287 | ±4.8 | 1" | 1.6 |
| 20 | 102100 | 2800 | 763 | 747000 | 90-255 | 556 | 32.5 | 305 | 902 | 292 | ±5.2 | 1" | 1.8 |
| 21 | 126070 | 2450 | 919 | 1016000 | 100-265 | 588 | 34.0 | 318 | 948 | 312 | ±5.4 | 1" | 1.8 |
| 22 | 146350 | 2150 | 1068 | 1386000 | 100-275 | 630 | 34.0 | 332 | 1008 | 344 | ±5.6 | 1" | 2.0 |
| 23 | 173830 | 2000 | 1235 | 1784000 | 100-290 | 655 | 35.5 | 348 | 1052 | 356 | ±6.0 | 1" | 2.0 |
Types of Couplings
A coupling is a device that connects two shafts and transmits power from one to the other. Its main purpose is to join two pieces of rotating equipment. It also allows for some degree of misalignment or end movement. Here are a few examples of coupling types: Beam coupling, Flexible coupling, Magnetic coupling, and Shaft coupling.
Beam coupling
Beam couplings are used to couple motors and other devices. They are available in several types, including flexible, slit, and rigid beam couplings. Each has unique properties and characteristics. These couplings are best for applications requiring a high level of precision and long life. They are also a practical solution for the connection of stepping and servo motors with screw rods.
Beam couplings are usually made of stainless steel or aluminum alloy, and feature spiral and parallel cut designs. Multiple cuts allow the coupling to accommodate multiple beams and improve angular and parallel misalignment tolerances. Additionally, beam couplings are comparatively cheaper than other types of rotary joints, and they require minimal maintenance.
The materials of a beam coupling should be considered early in the specification process. They are typically made of aluminum or stainless steel, but they can also be manufactured from Delrin, titanium, and other engineering grade materials. Beam couplings are often available in multiple sizes to fit specific shaft diameters.
Beam couplings are a key component of motion control systems. They provide excellent characteristics when used properly, and they are a popular choice for many applications. A thorough understanding of each type of coupling will help to prevent coupling failure and enhance system performance. Therefore, it is important to choose the right coupling for your application.
Various types of beam couplings have unique advantages and disadvantages. The FCR/FSR design has two sets of three beams. It is available in both metric and inch shaft sizes. The FCR/FSR couplings are ideal for light-duty power transmission applications. A metric shaft is more suitable for these applications, while an inch shaft is preferred for heavier duty applications.
Two types of beam couplings are available from Ruland. The Ruland Flexible beam coupling has a multi-helical cut design that offers a greater flexibility than commodity beam couplings. This design allows for higher torque capabilities while minimizing wind-up. In addition, it is also more durable than its commodity counterparts.
Flexible coupling
A flexible coupling is a versatile mechanical connection that allows for the easy coupling of two moving parts. The design of these couplings allows for a variety of stiffness levels and can address a variety of problems, such as torsional vibrations or critical speed. However, there are a number of tradeoffs associated with flexible couplings.
One of the biggest issues is the installation of the coupling, which requires stretching. This problem can be exacerbated by cold temperatures. In such a case, it is vital to install the coupling properly. Using a gear clamp is one of the most important steps in a successful installation. A gear clamp will keep the coupling in place and prevent it from leaking.
Another common type of flexible coupling is the gear coupling. These couplings are composed of two hubs with crowned external gear teeth that mesh with two internally splined flanged sleeves. The massive size of the teeth makes them resemble gears. Gear couplings offer good torque characteristics but require periodic lubrication. These couplings can also be expensive and have a limited number of applications.
Another type of flexible coupling is the SDP/SI helical coupling. These couplings can accommodate axial motion, angular misalignment, and parallel offset. This design incorporates a spiral pattern that makes them flexible. These couplings are available in stainless steel and aluminum.
A flexible coupling has a wide range of applications. Generally, it is used to connect two rotating pieces of equipment. Depending on its design, it can be used to join two pieces of machinery that move in different directions. This type of coupling is a type of elastomeric coupling, which has elastic properties.
There are many types of flexible couplings available for different types of applications. The purpose of a flexible coupling is to transmit rotational power from one shaft to another. It is also useful for transmitting torque. However, it is important to note that not all flexible couplings are created equally. Make sure to use a reputable brand for your coupling needs. It will ensure a reliable connection.
The simplest and most commonly used type of flexible coupling is the grid coupling. This type of coupling uses two hubs with slotted surfaces. The steel grid is allowed to slide along these slots, which gives it the ability to flex. The only limitation of this type of coupling is that it can only tolerate a 1/3 degree misalignment. It can transmit torques up to 3,656 Nm.
Magnetic coupling
Magnetic coupling is a technique used to transfer torque from one shaft to another using a magnetic field. It is the most common type of coupling used in machinery. It is highly effective when transferring torque from a rotating motor to a rotating shaft. Magnetic couplings can handle high torques and high speeds.
Magnetic coupling is described by the energy difference between a high-spin state and a broken symmetry state, with the former being the energy of a true singlet state. In single-determinant theories, this energy difference is called the Kij. Usually, the broken-symmetry state is a state with two interacting local high-spin centers.
The magnetic coupling device is regarded as a qualitative leap in the reaction still industry. It has solved a number of problems that had plagued the industry, including flammability, explosiveness, and leakage. Magnetic couplings are a great solution for many applications. The chemical and pharmaceutical industries use them for various processes, including reaction stills.
Magnetic couplings are a good choice for harsh environments and for tight spaces. Their enclosed design keeps them fluid and dust-proof. They are also corrosion-resistant. In addition, magnetic couplings are more affordable than mechanical couplings, especially in areas where access is restricted. They are also popular for testing and temporary installations.
Another use for magnetic coupling is in touch screens. While touch screens use capacitive and resistive elements, magnetic coupling has found a cool new application in wireless charging. While the finger tracking on touch screens may seem like a boley job, the process is very sensitive. The devices that use wireless charging need to have very large coils that are locked into resonant magnetic coupling.
Magnetic couplings also help reduce hydraulic horsepower. They cushion starts and reduce alignment problems. They can also improve flow in oversized pumps. A magnetic coupling with an 8 percent air gap can reduce hydraulic HP by approximately 27 percent. In addition, they can be used in aggressive environments. They also help reduce repair costs.
Magnetic couplings are a great choice for pumps and propeller systems because they have the added advantage of being watertight and preventing shaft failure. These systems also have the benefit of not requiring rotating seals.
Shaft coupling
A shaft coupling joins two shafts and transmits rotational motion. Generally, shaft couplings allow for some degree of misalignment, but there are also torque limiters. Selecting the right coupling can save you time and money and prevent equipment downtime. Here are the main features to consider when purchasing a coupling for your application.
Shaft couplings should be easy to install and disassemble, transmit full power to the mated shaft, and reduce shock loads. A shaft coupling that does not have projecting parts should be used for machines that move or rotate at high speeds. Some types of shaft couplings are flexible while others are rigid.
Shaft couplings can be used in a variety of applications, including piping systems. They can be used to connect shafts that are misaligned and help maintain alignment. They can also be used for vibration dampening. Shaft couplings also allow shafts to be disconnected when necessary.
Shaft couplings can accommodate a certain amount of backlash, but this backlash must be well within the tolerance set by the system. Extremely high backlash can break the coupling and cause excessive wear and stress. In addition, excessive backlash can lead to erratic alignment readings. To avoid these issues, operators must reduce backlash to less than 2deg.
Shaft couplings are often referred to by different names. Some are referred to as “sliced” couplings while others are known as “slit” couplings. Both types offer high torque and torsional stiffness. These couplings are typically made from metals with various alloys, such as acetal, stainless steel, or titanium.
CZPT Pulley produces shaft couplings for a variety of applications. These products are used in high-power transmission systems. They have several advantages over friction couplings. In addition to minimizing wear, they don’t require lubrication. They are also capable of transmitting high torque and high speeds.
Another type of shaft coupling is the universal coupling. It is used to transmit power to multiple machines with different spindles. Its keyed receiving side and flanges allow it to transmit power from one machine to another.

editor by czh 2022-12-29